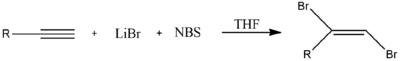Chemistry:1,2-Dibromoethylene
From HandWiki
|
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,2-Dibromoethene | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII |
| ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C2H2Br2 | |||
| Molar mass | 185.846 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | colorless liquid | ||
| Density | 2.246 g/cm3 | ||
| Boiling point | 110 °C (230 °F; 383 K) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Main hazards | Toxic | ||
| GHS pictograms |   
| ||
| GHS Signal word | Danger | ||
| H301, H314, H315, H319, H335 | |||
| P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+310, P301+330+331, P302+352, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P312, P321, P330, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P363, P403+233, P405, P501 | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
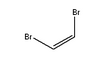
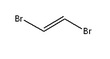
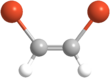
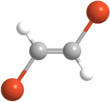
1,2-Dibromoethylene, also known as 1,2-dibromoethene and acetylene dibromide, is a dihalogenated unsaturated compound with one bromine on each of the two carbon atoms. There are two isomers of this compound, cis and trans. Both isomers are colorless liquids.
Synthesis
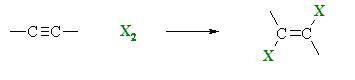
1,2-dibromoethylene can be synthesized by halogenation of acetylene C2H2 with bromine Br2.[1] In order to prevent the formation tetrahalogenated compounds, acetylene is used in excess, with Br2 as the limiting reagent.
Alternately, halogenation of this kind could also be achieved through the use of two equivalents of N-bromosuccinimide and lithium bromide (LiBr). N-Bromosuccinimide provides Br+ as an electrophile, which is followed by Br− from LiBr.[2]
References
- ↑ "Chapter 9: Addition Reactions of Alkynes". McGraw-Hill. http://www.mhhe.com/physsci/chemistry/carey/student/olc/ch09additionreactionsofalkynes.html.
- ↑ Shao, L.-X.; Shi, M. (2006). "N-Bromosuccinimide and Lithium Bromide: An Efficient Combination for the Dibromination of Carbon–Carbon Unsaturated Bonds". Synlett 2006 (8): 1269–1271. doi:10.1055/s-2006-941558. https://www.thieme-connect.de/products/ejournals/pdf/10.1055/s-2006-941558.pdf.