Chemistry:1,2-Dinitrobenzene
From HandWiki
| |||
|
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,2-Dinitrobenzene | |||
| Other names
ortho-dinitrobenzene
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 3443 1597 | ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C6H4N2O4 | |||
| Molar mass | 168.108 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | white solid | ||
| Density | 1.565 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | 118 °C (244 °F; 391 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 318 °C (604 °F; 591 K) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS pictograms |   
| ||
| GHS Signal word | Danger | ||
| H300, H310, H330, H373, H410 | |||
| P260, P262, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P284, P301+310, P302+350, P304+340, P310, P314, P320, P321, P322, P330, P361, P363, P391, P403+233, P405, P501 | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Tracking categories (test):
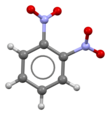
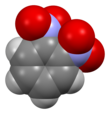
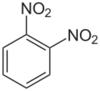
1,2-Dinitrobenzene is one of three isomers of dinitrobenzene, with the formula C6H4(NO2)2. The compound is a white or colorless solid that is soluble in organic solvents. It is prepared from 2-nitroaniline by diazotization and treatment with sodium nitrite in the presence of a copper catalyst.[1]
References
- ↑ E. B. Starkey (1939). "p-Dinitrobenzene". Org. Synth. 19: 40. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.019.0040.
 |