Chemistry:2,4,5-Trichlorophenol
From HandWiki
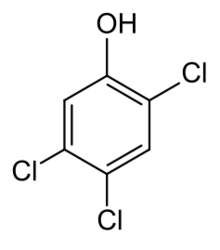
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,4,5-Trichlorophenol | |
| Other names
Dowicide 2, Collunosol
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 607569 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| 102425 | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2020 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H3Cl3O | |
| Molar mass | 197.44 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 68.4 °C (155.1 °F; 341.5 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 262 °C (504 °F; 535 K)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H302, H315, H319, H410 | |
| P264, P270, P273, P280, P301+312, P302+352, P305+351+338, P321, P330, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P391, P501 | |
| Flash point | 133 °C (271 °F; 406 K) cc |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
2,4-Dichlorophenol, 1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene, 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
2,4,5-Trichlorophenol (TCP) is an organochloride with the molecular formula C6H3Cl3O. It has been used as a fungicide and herbicide.[2] Precursor chemical used in the production of 2,4,5-Trichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4,5-T) and hexachlorophene involves the intermediate production of 2,4,5-trichlorophenol (TCP) and the formation of 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzodioxin2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD, commonly referred to simply as dioxin) as an unwanted by-product. In the course of purifying the hexachlorophene, still bottom wastes were created with concentrated levels of TCP and dioxin.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Haynes, p. 3.522
- ↑ "Hazard Summary – 2,4,5-Trichlorophenol". United States Environmental Protection Agency. https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2016-09/documents/2-4-5-trichlorophenol.pdf.
Cited sources
- Haynes, William M., ed (2016). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (97th ed.). CRC Press. ISBN 9781498754293.
See also
 |

