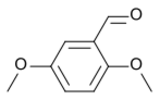
Chemistry:2,5-Dimethoxybenzaldehyde
From HandWiki
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,5-Dimethoxybenzaldehyde | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H10O3 | |
| Molar mass | 166.17 g/mol |
| Appearance | Yellow crystalline solid |
| Density | 1.114 g/mL |
| Melting point | 50 °C (122 °F; 323 K) |
| Boiling point | 283.8 °C (542.8 °F; 557.0 K) |
| Hazards[1] | |
| Main hazards | Irritant |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H315, H319, H334, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P285, P302+352, P304+340, P304+341, P305+351+338, P312, P332+313, P337+313, P342+311, P362, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 110 °C (230 °F; 383 K) (c.c.) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
2,5-Dimethoxybenzaldehyde is an organic compound and a benzaldehyde derivative. One of its uses is the production of 2,5-dimethoxyphenethylamine, also known as 2C-H. 2C-H is used to produce many other substituted phenethylamines such as 2C-B, 2C-I and 2C-C.[2]
References
- ↑ "2,5-Dimethoxybenzaldehyde" (in en). https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/66726#section=Safety-and-Hazards.
- ↑ Shulgin, Alexander; Shulgin, Ann (September 1991). PiHKAL: A Chemical Love Story. Berkeley, California: Transform Press. ISBN 0-9630096-0-5. OCLC 25627628. http://www.erowid.org/library/books_online/pihkal/pihkal.shtml.
 |


