Chemistry:2-Chloropropylene
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
2-chloropropene
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2456 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H5Cl | |
| Molar mass | 76.52 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless gas |
| Density | 0.9017 g/mL (20 °C) |
| Melting point | −137.4 °C (−215.3 °F; 135.8 K) |
| Boiling point | 22.6 °C (72.7 °F; 295.8 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H224, H302, H312, H315, H319, H332, H335 | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+312, P302+352, P303+361+353, P304+312, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P322, P330, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P363 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
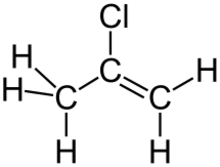
2-Chloropropylene is an organochlorine compound with the formula CH2=C(Cl)CH3. It is a colorless gas that condenses just below room temperature. Unlike the closely related vinyl chloride, which is a major industrial chemical, 2-chloropropene has no commercial applications and is a lightly studied compound. In the research laboratory, it is used as a source of the 2-propenyl group.[1] One early synthesis involves dehydrohalogenation of 1,2-dichloropropane with potassium hydroxide.[2]
References
- ↑ Takahashi, Tamotsu; Kotora, Martin; Fischer, Reinald; Nishihara, Yasushi; Nakajima, Kiyohiko (1995). "Oxidative Addition of 2-Haloalkene to Zirconocene". Journal of the American Chemical Society 117 (44): 11039–11040. doi:10.1021/ja00149a040.
- ↑ Goudet, Henry; Schenker, Fritz (1927). "Recherches sur quelques dérivés du propylène". Helvetica Chimica Acta 10: 132–140. doi:10.1002/hlca.19270100117.
 |

