Chemistry:2-Methyl-2-butene
From HandWiki
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Methylbut-2-ene | |
| Other names
β-Isoamylene
Trimethylethylene 2-Methyl-2-butene Isoamylene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2460 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H10 | |
| Molar mass | 70.1329 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | Sweet |
| Density | 0.662 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −134 °C (−209 °F; 139 K) |
| Boiling point | 39 °C (102 °F; 312 K) |
| Slightly soluble | |
| Solubility in alcohols, ether | Miscible |
| -54.14·10−6 cm3/mol | |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.385 |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Mildly toxic |
| Flash point | < −45 °C (−49 °F; 228 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
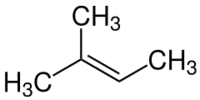
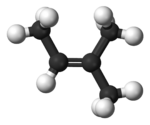
2-Methyl-2-butene, 2m2b, 2-methylbut-2-ene, also beta-isoamylene is an alkene hydrocarbon with the molecular formula C5H10.
Used as a free radical scavenger in trichloromethane (chloroform) and dichloromethane (methylene chloride). It is also used to scavenge hypochlorous acid (HOCl) in the Pinnick oxidation.
John Snow, the English physician, experimented with it in the 1840s as an anesthetic, but stopped using it for unknown reasons.[4]
See also
References
- ↑ Dean's Handbook of Organic Chemistry, 2nd Edition.
- ↑ "Safety (MSDS) data for 2-methyl-2-butene". http://msds.chem.ox.ac.uk/ME/2-methyl-2-butene.html.
- ↑ PubChem
- ↑ Caton, Donald (2000). "John Snow's practice of obstetric anesthesia". Anesthesiology: The Journal of the American Society of Anesthesiologists 92 (1): 247–252. doi:10.1097/00000542-200001000-00037. PMID 10638922.
 |

