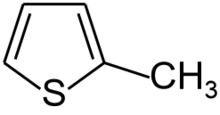
Chemistry:2-Methylthiophene
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Methylthiophene | |
| Other names
Methylthiol
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H6S | |
| Molar mass | 98.16 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Density | 1.0168 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −63.4 °C (−82.1 °F; 209.8 K) |
| Boiling point | 112.6 °C (234.7 °F; 385.8 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H225, H302, H312, H332 | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+312, P302+352, P303+361+353, P304+312, P304+340, P312, P322, P330, P363, P370+378, P403+235, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
2-Methylthiophene is an organosulfur compound with the formula CH3C4H3S. It is a colorless, flammable liquid. It can be produced by Wolff-Kishner reduction of thiophene-2-carboxaldehyde.[1] Its commercial synthesis involvess vapor-phase dehydrogenation of a 1-pentanol/CS2 mixture.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ King, Wm. J.; Nord, F. F. (1949). "Thiophene Series. V. Wolff-Kishner Reductions". Journal of Organic Chemistry 14: 638–42. doi:10.1021/jo01156a016.
- ↑ Swanston, Jonathan (2006). "Thiophene". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a26_793.pub2. ISBN 3527306730..
 |

