Chemistry:2-Phosphoglyceric acid
From HandWiki
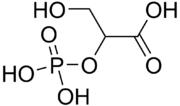
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3-hydroxy-2-phosphonooxypropanoic acid
| |
| Other names
2PG
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H7O7P | |
| Molar mass | 186.06 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
2-Phosphoglyceric acid (2PG), or 2-phosphoglycerate, is a glyceric acid which serves as the substrate in the ninth step of glycolysis. It is catalyzed by enolase into phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP), the penultimate step in the conversion of glucose to pyruvate.
In glycolysis
| 3-phospho-D-glycerate | Phosphoglyceromutase | 2-phospho-D-glycerate | Enolase | phosphoenolpyruvate | ||
| 90px | image:2-phospho-D-glycerate wpmp.png | image:phosphoenolpyruvate wpmp.png | ||||
| H2O | ||||||
| 75px | 75px | |||||
| H2O | ||||||
| Phosphoglyceromutase | Enolase | |||||
Compound C00197 at KEGG Pathway Database. Enzyme 5.4.2.1 at KEGG Pathway Database. Compound C00631 at KEGG Pathway Database. Enzyme 4.2.1.11 at KEGG Pathway Database. Compound C00074 at KEGG Pathway Database.
See also
References
 |

