Chemistry:3-Methylhistidine
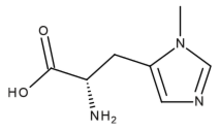
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2S)-2-Amino-3-(1-methyl-1H-imidazol-5-yl)propanoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 83651 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| 1568650 | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H11N3O2 | |
| Molar mass | 169.184 |
| 200 mg/mL at 25 °C[1][2] | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
3-Methylhistidine (3-MH) is a post-translationally modified amino acid which is excreted in human urine.[1][2] Urinary concentration of 3-methylhistidine is a biomarker for skeletal muscle protein breakdown in humans who have been subject to muscle injury.[1][3][4] Urinary 3-methylhistidine concentrations are also elevated from consumption of soy-based products and meat, particularly chicken.[1]
Biochemistry
3-Methylhistidine is a metabolic product that is produced in the body via the enzymatic methylation of histidine during peptide bond synthesis and the methylation of actin and myosin.[1][2]
Detection in body fluids
The normal concentration of 3-methylhistidine in the urine of healthy adult humans has been detected and quantified in a range of 3.63–69.27 micromoles per millimole (μmol/mmol) of creatinine, with most studies reporting the average urinary concentration between 15–20 μmol/mmol of creatinine.[1] The average concentration of 3-methylhistidine in human blood plasma has been detected and quantified at 2.85 micromolar (μM) with a range of 0.0–5.9 μM.[1] The average concentration of 3-methylhistidine in human cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) has been detected and quantified at 3.82 μM with a range of 1.39–6.25 μM.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 "3-Methylhistidine". HMDB Version 4.0. Human Metabolome Database. 20 December 2017. http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB00479.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "3-Methyl-L-histidine". 3-Methyl-L-histidine. United States National Library of Medicine – National Center for Biotechnology Information. 23 December 2017. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/64969. Retrieved 25 December 2017.
- ↑ "Methods for measuring tissue protein breakdown rate in vivo". Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolic Care 8 (5): 534–537. September 2005. doi:10.1097/01.mco.0000170754.25372.37. PMID 16079625.
- ↑ "Measuring protein breakdown rate in individual proteins in vivo". Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolic Care 13 (5): 526–531. September 2010. doi:10.1097/MCO.0b013e32833c3c64. PMID 20616712.
 |

