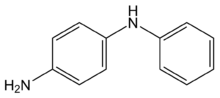
Chemistry:4-Aminodiphenylamine
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
N1-Phenylbenzene-1,4-diamine | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 908935 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| 241334 | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1673 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H12N2 | |
| Molar mass | 184.242 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | purple–black or dark purple |
| Density | 1.09 g/mL |
| Melting point | 75 °C (167 °F; 348 K) |
| Boiling point | 354 °C (669 °F; 627 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H302, H317, H319, H410 | |
| P261, P264, P270, P272, P273, P280, P301+312, P302+352, P305+351+338, P321, P330, P333+313, P337+313, P363, P391, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
4-Aminodiphenylamine is a diphenylamine with an additional amine substituent. This dimer of aniline has various industrial uses, including as a hair dye ingredient, but also has raised concerns about toxicity by skin contact.[1] It is also a starting material for the synthesis of 6PPD, an antiozonant for various rubber products.[2] A colorimetric test for the quantitative analysis of nitrite, at levels below 100 nanograms per milliliter, is based on nitrite-catalyzed coupling of 4-aminodiphenylamine with N,N-dimethylaniline.[3]
The most common route of industrial production is by the reaction of aniline with 4‑nitrochlorobenzene followed by reduction of the intermediate 4‑nitrodiphenylamine.[4] An alternative is the direct condensation reaction of nitrobenzene with aniline via a nucleophilic aromatic substitution of hydrogen,[5] this again requires a reduction step.[4]
References
- ↑ Khanna, S. K.; Tewari, Pushpa; Joshi, Anil; Singh, G. B. (1987). "Studies on the skin uptake and efflux kinetics of N-phenyl-p-phenylenediamine: an aromatic amine intermediate". International Journal of Cosmetic Science 9 (3): 137–147. doi:10.1111/j.1467-2494.1987.tb00470.x. PMID 19456976.
- ↑ Engels, Hans-Wilhelm; Weidenhaupt, Herrmann‐Josef; Pieroth, Manfred; Hofmann, Werner; Menting, Karl‐Hans; Mergenhagen, Thomas; Schmoll, Ralf; Uhrlandt, Stefan (2007). "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a23_365.pub2.
- ↑ Kadowaki, Ryoichi; Nakano, Shigenori; Kawashima, Takuji (1999). "Sensitive flow injection colorimetry of nitrite by catalytic coupling of N-phenyl-p-phenylenediamine with N,N-dimethylaniline". Talanta 48 (1): 103–107. doi:10.1016/s0039-9140(98)00227-6. PMID 18967448.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Bochkarev, V.V.; Soroka, L.S.; Bashkin, J.K. (December 2016). "Resource-efficient technology to produce 4-aminodiphenylamine". Resource-Efficient Technologies 2 (4): 215–224. doi:10.1016/j.reffit.2016.10.011.
- ↑ Stern, Michael K.; Hileman, Fredrick D.; Bashkin, James K. (November 1992). "The direct coupling of aniline and nitrobenzene: a new example of nucleophilic aromatic substitution for hydrogen". Journal of the American Chemical Society 114 (23): 9237–9238. doi:10.1021/ja00049a095.
 |
