Chemistry:4-Mercaptophenylacetic acid
From HandWiki
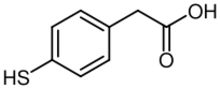
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-(4-sulfanylphenyl)acetic acid
| |
| Preferred IUPAC name
(4-Sulfanylphenyl)acetic acid | |
| Other names
2-(4-Mercaptophenyl)acetic acid
4-Mercaptophenylacetic acid MPAA | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| HSC6H4CH2CO2H | |
| Molar mass | 168.21 g/mol |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H315, H318, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P312, P321, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
MPAA (4-Mercaptophenylacetic acid) is a redox buffer that increases the folding rate of disulfide-containing proteins.
MPAA is also used in native chemical ligation as a thiol catalyst.
This article does not cite any external source. HandWiki requires at least one external source. See citing external sources. (2021) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
 |

