Chemistry:Ammonium thiosulfate
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Diammonium thiosulfate
| |
| Other names
Ammonium thiosulphate, ATS
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
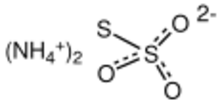
| [NH 4] 2S 2O 3 | |
| Molar mass | 148.20 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless or white, hygroscopic solid |
| Density | 1.679 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | decomposes at 100 °C |
| 173 g/100 mL (20 °C) | |
| Solubility | slightly soluble in acetone insoluble in alcohol |
| Structure | |
| monoclinic | |
| Hazards | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
2980 mg/kg (rat, oral) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Ammonium thiosulfate (ammonium thiosulphate in British English) is an inorganic compound with the formula [NH
4]
2S
2O
3. It is white crystalline solid with ammonia odor, readily soluble in water, slightly soluble in acetone and insoluble in ethanol and diethyl ether.[1]
Production
It is produced by treating ammonium sulfite with sulfur at temperatures between 85 and 110 °C:[2]
- [NH
4]
2SO
3 + S → [NH
4]
2S
2O
3
Applications
Ammonium thiosulfate is used in photographic fixer. It is a so-called rapid fixer, acting more quickly than sodium thiosulfate fixers.[3] Fixation involves these chemical reactions (illustrated for silver bromide):[4]
- AgBr + 2 [NH
4]
2S
2O
3 → [NH
4]
3[Ag(S
2O
3)
2] + [NH
4]Br - AgBr + 3 [NH
4]
2S
2O
3 → [NH
4]
5[Ag(S
2O
3)
3] + [NH
4]Br
Ammonium thiosulfate is also used for leaching of gold and silver. It works with presence of copper as a catalyst here. This process is a nontoxic alternative gold cyanidation.[5] The advantage to ammonium thiosulfate is that the pyrolysis of its silver complexes leaves a residue solely of silver sulfide, in contrast to complexes derived from sodium thiosulfate.[2]
Other
Ammonium thiosulfate can be used as a fertilizer.[6] As suggested by some research studies, it can also be used as an additive to coal-waste mixtures to reduce formation of dioxins and furans during combustion.[7]
Safety
LD50 (oral, rat) is 2890 mg/kg.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ MSDS - Ammonium Thiosulfate
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 J. J. Barbera; A. Metzger; M. Wolf (2012). "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a25_477.
- ↑ "Praní černobílých filmů a papírů". http://www.paladix.cz/clanek.php?aid=10304&sid=1&hledej=.
- ↑ Keller, Karlheinz (2005). "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a20_001.
- ↑ Aylmore, M.G; Muir, D.M (2001). "Thiosulfate leaching of gold—A review". Minerals Engineering 14 (2): 135–174. doi:10.1016/S0892-6875(00)00172-2. Bibcode: 2001MiEng..14..135A.
- ↑ McCarty, G. W.; Bremner1, J. M.; Krogmeier1, M. J. (1990). "Evaluation of ammonium thiosulfate as a soil urease inhibitor". Fertilizer Research 24 (3): 135–139. doi:10.1007/BF01073581.
- ↑ Wielgosiński, Grzegorz (2011). "The Reduction of Dioxin Emissions from the Processes of Heat and Power Generation". Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association 61 (5): 511–526. doi:10.3155/1047-3289.61.5.511. PMID 21608491. Bibcode: 2011JAWMA..61..511W.
 |

