Chemistry:Beauvericin
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
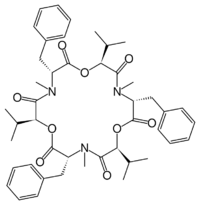
(3S,6R,9S,12R,15S,18R)-3,9,15-Tribenzyl-6,12,18-triisopropyl-4,10,16-trimethyl-1,7,13-trioxa-4,10,16-triazacyclooctadecane-2,5,8,11,14,17-hexone
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C45H57N3O9 | |
| Molar mass | 783.963 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Beauvericin is a depsipeptide with antibiotic and insecticidal effects belonging to the enniatin family. It was isolated from the fungus Beauveria bassiana, but is also produced by several other fungi, including several Fusarium species;[1][2] it may therefore occur in grain (such as corn, wheat and barley) contaminated with these fungi.[2][3][4] Beauvericin is active against Gram-positive bacteria and mycobacteria, and is also capable of inducing programmed cell death in mammals.[2]
Chemically, beauvericin is a cyclic hexadepsipeptide with alternating N-methyl-phenylalanyl and D-hydroxy-iso-valeryl residues. Its ion-complexing capability allows beauvericin to transport alkaline earth metal and alkali metal ions across cell membranes.[citation needed]
Beauvericin has in vitro fungicidal effects on Candida parapsilosis when used in combination with the antifungal drug ketoconazole at dosages of 0.1 μg/ml. Increased survivability rates and low cytotoxicity were also observed in mouse models.[5]
References
- ↑ "The structure of beauvericin, a new depsipeptide antibiotic toxic to Artemia salina". Tetrahedron Letters 10 (49): 4255–4258. 1969. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(01)88668-8.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Logrieco A; Moretti A; Castella G et al. (1998). "Beauvericin Production by Fusarium Species". Appl Environ Microbiol 64 (8): 3084–8. doi:10.1128/AEM.64.8.3084-3088.1998. PMID 9687479. Bibcode: 1998ApEnM..64.3084L.
- ↑ "Occurrence of Beauvericin and Enniatins in Wheat Affected by Fusarium avenaceum Head Blight". Appl Environ Microbiol 68 (1): 82–5. 2002. doi:10.1128/AEM.68.1.82-85.2002. PMID 11772612. Bibcode: 2002ApEnM..68...82L.
- ↑ "Presence and concentrations of the Fusarium-related mycotoxins beauvericin, enniatins and moniliformin in finnish grain samples". Food Additives and Contaminants 21 (8): 794–802. 2004. doi:10.1080/02652030410001713906. PMID 15370831.
- ↑ Zhang L; Yan K; Zhang Y; Huang R; Bian J; Zheng C; Sun H; Chen Z et al. (2007). "High-throughput synergy screening identifies microbial metabolites as combination agents for the treatment of fungal infections". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104 (11): 4606–11. doi:10.1073/pnas.0609370104. PMID 17360571. Bibcode: 2007PNAS..104.4606Z.
 |

