Chemistry:Borirane
From HandWiki
|
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
|---|---|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
| ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| BC2H5 | |||
| Molar mass | 39.872 g mol−1 | ||
| Melting point | −129 °C (−200 °F; 144 K) | ||
| Boiling point | −24 °C (−11 °F; 249 K) | ||
| 15.425 g dm−3 | |||
| Related compounds | |||
Related heterocycles
|
Aziridine Ethylene oxide Thiirane | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
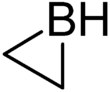
Borirane is a heterocyclic organic compound with the formula C2H4BH. This colourless, flammable gas is the simplest borirane, a three-membered ring consisting of two carbon and one boron atom. It can be viewed as a structural analog of aziridine, with boron replacing the nitrogen atom of aziridine. Borirane is isomeric with ethylideneborane.
This compound has five isomers.[1]
References
- ↑ Stone, F. G. A.; Abel, E. W. (1987). Organometallic Chemistry. 16. London: Royal Society of Chemistry. pp. 40. ISBN 9780851866413. https://books.google.com/books?id=LvvrQW1mKewC&q=Borirane+uses&pg=PA40.
 |