Chemistry:Cobalt laurate
From HandWiki
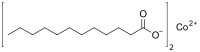
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Cobalt dodecanoate
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C24H48CoO4 | |
| Molar mass | 459.6 |
| Insoluble | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Cobalt laurate is an metal-organic compound with the chemical formula C24H48CoO4.[1] It is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid (lauric acid).
Synthesis
Cobalt laurate can be prepared by the reaction of aqueous solutions of cobalt(II) chloride (CoCl2) with sodium laurate.[2]
Physical properties
Cobalt laurate forms dark violet crystals.[3]
It does not dissolve in water,[4] but is soluble in alcohol.
References
- ↑ Levy, Jean-Claude Serge (3 September 2018) (in en). Magnetic Structures of 2D and 3D Nanoparticles: Properties and Applications. CRC Press. p. 216. ISBN 978-1-315-36135-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=UIuADwAAQBAJ&dq=cobalt+laurate&pg=PA216. Retrieved 26 January 2023.
- ↑ Zhang, Yajing; Zhu, Yuan; Wang, Kangjun; Li, Da; Wang, Dongping; Ding, Fu; Meng, Dan; Wang, Xiaolei et al. (June 2018). "Controlled synthesis of Co2C nanochains using cobalt laurate as precursor: Structure, growth mechanism and magnetic properties". Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 456: 71–77. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2018.02.014. Bibcode: 2018JMMM..456...71Z.
- ↑ (in en) Theses, Chemistry. Johns Hopkins University. 1889. p. 27. https://books.google.com/books?id=AjXAJVwi5ycC&dq=cobalt+laurate&pg=RA5-PA27. Retrieved 26 January 2023.
- ↑ Benedikt, R. (1895) (in en). Chemical analysis of oils, fats, waxes. p. 11. https://books.google.com/books?id=nhcWkACYl4gC&dq=cobalt+laurate&pg=PA11. Retrieved 26 January 2023.
 |

