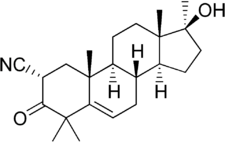
Chemistry:Cyanoketone
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Cyanotrimethylandrostenolone; CTM; 2α-Cyano-4,4',17α-trimethylandrost-5-en-17β-ol-3-one |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H33NO2 |
| Molar mass | 355.522 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Cyanoketone, also known as 2α-cyano-4,4',17α-trimethylandrost-5-en-17β-ol-3-one (CTM),[1] is a synthetic androstane steroid and a steroidogenesis inhibitor which is used in scientific research.[2][3][4] On account of its structural similarity to pregnenolone, cyanoketone binds to and acts as a potent, selective, and irreversible inhibitor of 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (3β-HSD),[1][5] an enzyme that is responsible for the conversion of pregnenolone into progesterone, 17α-hydroxypregnenolone into 17α-hydroxyprogesterone, DHEA into androstenedione, and androstenediol into testosterone.[2][3][6] As such, cyanoketone inhibits the production of both gonadal and adrenal steroids, including progesterone,[5] androgens, estrogens, and corticosteroids.[3][6] The drug is too toxic for therapeutic use in humans, and so has been used instead exclusively as a research tool.[2][3]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 General, Comparative and Clinical Endocrinology of the Adrenal Cortex. Elsevier Science. 22 October 2013. pp. 136–. ISBN 978-1-4832-5980-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=iHrAAgAAQBAJ&pg=PA136.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Principles of Endocrine Pharmacology. Springer Science & Business Media. 6 December 2012. pp. 280–. ISBN 978-1-4684-5036-1. https://books.google.com/books?id=mTagBQAAQBAJ&pg=PA280.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Principles of Endocrine Pharmacology. Springer Science & Business Media. 6 December 2012. pp. 11–12. ISBN 978-1-4684-5036-1. https://books.google.com/books?id=mTagBQAAQBAJ&pg=PA11.
- ↑ "Inhibition of steroidogenesis by cyanoketone". Gynecologic Investigation 2 (1): 309–315. 1971. doi:10.1159/000301873. PMID 4266510.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Preimplantation Embryo Development. Springer Science & Business Media. 6 December 2012. pp. 30–. ISBN 978-1-4613-9317-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=1I-1BwAAQBAJ&pg=PA30.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Vertebrate Endocrinology. Academic Press. 4 May 2013. pp. 71–. ISBN 978-0-12-396465-6. https://books.google.com/books?id=F_NaW1ZcSSAC&pg=PA71.
 |

