Chemistry:Dehydroretinal
From HandWiki
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
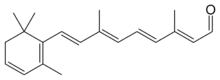
| IUPAC name
3,4-Didehydroretinal
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2E,4E,6E,8E)-3,7-Dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohexa-1,3-dien-1-yl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenal | |
| Other names
3,4-Dehydroretinal; 3,4-Didehydroretinaldehyde
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 3DMet | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Dehydroretinal |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H26O | |
| Molar mass | 282.427 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Dehydroretinal (3,4-dehydroretinal) is a derivative metabolite of retinal[1] belonging to the group of vitamin A2 as a retinaldehyde form, besides the endogenously present 3,4-dehydroretinol and 3,4-dehydroretinoic acid.[2][3]
The livers of some freshwater fishes and some fish found in India contain a higher ratio of dehydroretinal to retinal than do other species.[4][5]
See also
References
- ↑ Gibney, Michael J.; Margetts, Barrie M.; Kearney, John M. et al., eds. (2012), Public Health Nutrition, John Wiley & Sons, p. 210, ISBN 978-1118574225, https://books.google.com/books?id=WtRFYyts5IwC&pg=PA210
- ↑ "Biosynthesis of 3-dehydroretinol (vitamin A2) from all-trans-retinol (vitamin A1) in human epidermis". J. Invest. Dermatol. 85 (6): 498–500. 1985. doi:10.1111/1523-1747.ep12277290. PMID 4067325.
- ↑ "The identification of dehydroretinol (vitamin A2) in human skin". Experientia 36 (3): 317–318. 1980. doi:10.1007/bf01952299. PMID 7371787.
- ↑ "Ling cod and other fish liver oils rich in vitamin A2". Biochem J 40 (5–6): lix. 1946. PMID 20277273.
- ↑ Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (1967), Requirements of Vitamin A, Thiamine, Riboflavin & Niacin: Report of a Joint Fao-Who Expert Group, United Nations, p. 26, ISBN 9251004536, https://books.google.com/books?id=mXHCL4M0FNMC&pg=PA26
 |
