Chemistry:Diethyl dixanthogen disulfide
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
O1,O3-Diethyl 2-(dithioperoxy)-1,3-dithiodicarbonic acid | |
| Other names
Auligen, Antigal, Dixanthogen
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H10O2S4 | |
| Molar mass | 242.38 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | yellow solid |
| Density | 1.23 g/cm3[1] |
| Melting point | 30 °C (86 °F; 303 K) |
| Pharmacology | |
| 1=ATC code }} | P03AA01 (WHO) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
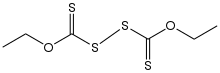
Diethyl dixanthogen disulfide is the organosulfur compound with the formula (C
2H
5OC(S)S)
2. It is one of the most common dixanthogen disulfides, compounds of the type (ROC(S)S)
2 (R = alkyl). A yellow solid, It is obtained by oxidation of sodium ethylxanthate or potassium ethylxanthate.[2][3]
According to X-ray crystallography, the two C
2H
5OC(S)S) groups in solid diethyl dixanthogen disulfide are planar and are linked by a disulfide bond. The C-S-S-C dihedral angle is near 90°, as is common for acyclic disulfides.[1]
Occurrence and reactions
Diethylxanthogen reacts with aqueous base to regenerate the xanthate, at least partially.[4]
Diethylxanthogen arises by oxidation of xanthates during froth flotation. Diethylxanthogens are thought to participate in the flotation of certain sulfide minerals.[5]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Watanabe, Y. (1971). "The crystal structure of diethyldixanthogen". Acta Crystallographica Section B Structural Crystallography and Crystal Chemistry 27 (3): 644–649. doi:10.1107/S056774087100270X.
- ↑ Weber, Wolfgang G.; McLeary, James B.; Sanderson, Ron D. (2006). "Facile Preparation of Bis(thiocarbonyl)disulfides via Elimination". Tetrahedron Letters 47 (27): 4771–4774. doi:10.1016/j.tetlet.2006.04.031.
- ↑ Schroll, Alayne L.; Barany, George (1986). "Novel Symmetrical and Mixed Carbamoyl and Aminopolysulfanes by Reactions of (Alkoxydichloromethyl)polysulfanyl Substrates with N-Methylaniline". The Journal of Organic Chemistry 51 (10): 1866–1881. doi:10.1021/jo00360a039.
- ↑ Jones, M.H.; Woodcock, J.T. (1983). "Decomposition of Alkyl Dixanthogens in Aqueous Solutions". International Journal of Mineral Processing 10: 1–24. doi:10.1016/0301-7516(83)90030-3.
- ↑ Leppinen, J.O. (1990). "FTIR and Flotation Investigation of the Adsorption of Ethyl Xanthate on Activated and Non-Activated Sulfide Minerals". International Journal of Mineral Processing 30 (3–4): 245–263. doi:10.1016/0301-7516(90)90018-T.
 |

