Chemistry:Dimethylaminophosphorus dichloride
From HandWiki
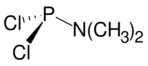
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
dimethylaminochlorophosphine, dimethylphosphoramidous dichloride
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2H6Cl2NP | |
| Molar mass | 145.95 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Density | 1.264 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 40 °C (104 °F; 313 K) 10 torr |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H225, H314 | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P260, P264, P280, P301+330+331, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P321, P363, P370+378, P403+235, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Dimethylaminophosphorus dichloride is an organophosphorus compound with the formula Me2NPCl2 (Me = methyl). A colorless liquid, it is a reagent in the preparation of other organophosphorus compounds. Many analogous compounds can be prepared from the reactions of secondary amines and phosphorus trichloride:[1]
- 2 R2NH + PCl3 → R2NPCl2 + R2NH2Cl
Reactions
Further equivalents of amine react with dialkylaminophosphorus dichlorides:
- 2 R2NH + R2NPCl2 → (R2N)2PCl + R2NH2Cl
Since the P-NR2 bond is not attacked by Grignard reagents, dimethylaminophosphorus dichloride can be selectively dimethylated:
- 2 MeMgBr + Me2NPCl2 → Me2NPMe2 + 2 MgBrCl
The resulting dimethylphosphino derivative, a structural relative of tetramethylhydrazine, reacts with hydrogen chloride to give chlorodimethylphosphine:[2]
- Me2NPMe2 + 2 HCl → ClPMe2 + Me2NH2Cl
References
- ↑ Morse, J. G.; Cohn, K.; Rudolph, R. W.; Parry, R. W. (1967). "Substituted Difluoro- and Dichlorophosphines". Inorganic Syntheses 22: 147–156. doi:10.1002/9780470132418.ch22.
- ↑ Burg, Anton B.; Slota, Peter J. (1958). "Dimethylaminodimethylphosphine". Journal of the American Chemical Society 80 (5): 1107–1109. doi:10.1021/ja01538a023.
 |

