Chemistry:Disodium guanylate
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Disodium 5′-guanylate
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
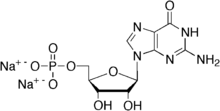
Disodium [(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(2-amino-4-oxo-2,3-dihydro-9H-purin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl phosphate | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H12N5Na2O8P | |
| Molar mass | 407.186 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Disodium guanylate, also known as sodium 5'-guanylate and disodium 5'-guanylate, is a natural sodium salt of the flavor enhancing nucleotide guanosine monophosphate (GMP). Disodium guanylate is a food additive with the E number E627.[2] It is commonly used in conjunction with glutamic acid.
As it is a fairly expensive additive, it is usually not used independently of glutamic acid; if disodium guanylate is present in a list of ingredients but MSG does not appear to be, it is likely that glutamic acid is provided as part of another ingredient such as a processed soy protein complex. It is often added to foods in conjunction with disodium inosinate; the combination is known as disodium 5'-ribonucleotides.
Disodium guanylate is produced by fermentation.[3][4] It is often added to instant noodles, potato chips and other snacks, savory rice, tinned vegetables, cured meats, and packaged soup.
See also
References
- ↑ "SID 164216535 - PubChem". https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/164216535.
- ↑ E627 : Sodium guanylate
- ↑ Conn, Helen (1 February 1992). ""Umami": The Fifth Basic Taste". Nutrition & Food Science 92 (2): 21–23. doi:10.1108/EUM0000000000953.
- ↑ Kinoshita, Kazumoto; Shiro, Teruo; Yamazaki, Akihiro; Kumashiro, Izumi; Takenishi, Tadao; Tsunoda, Toshinao (July 1967). "Industrial production of disodium 5?-guanylate". Biotechnology and Bioengineering 9 (3): 329–342. doi:10.1002/bit.260090306.
 |
