Chemistry:Fluopyram
From HandWiki
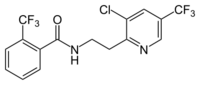
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
N-{2-[3-Chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-2-yl]ethyl}-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzamide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H11ClF6N2O | |
| Molar mass | 396.72 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 117.5 °C (243.5 °F; 390.6 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 318–321 °C (604–610 °F; 591–594 K)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Fluopyram is a fungicide and nematicide used in agriculture.[2][3] It is used to control fungal diseases such as gray mold (Botrytis cinerea), powdery mildew, apple scab, Alternaria, Sclerotinia, and Monilinia. It is an inhibitor of succinate dehydrogenase (SDHI fungicide).[4]
Developed and produced by Bayer, it was approved in 2012 by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency[4] and in 2013 it was approved in the EU for use as an active ingredient in pesticides.[5]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Fluopyram". Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. http://www.fao.org/fileadmin/templates/agphome/documents/Pests_Pesticides/JMPR/Evaluation10/Fluopyram.pdf.
- ↑ Grabau, Zane J.; Liu, Chang; Schumacher, Lesley A.; Small, Ian M.; Wright, David L. (February 2021). "In-furrow fluopyram nematicide efficacy for Rotylenchulus reniformis management in cotton production". Crop Protection 140: 105423. doi:10.1016/j.cropro.2020.105423.
- ↑ Faske, TR; Hurd, K (December 2015). "Sensitivity of Meloidogyne incognita and Rotylenchulus reniformis to Fluopyram.". Journal of Nematology 47 (4): 316–21. PMID 26941460.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "Fluopyram". New Active Ingredient Review. Minnesota Department of Agriculture. April 2012. http://www.mda.state.mn.us/chemicals/pesticides/regs/~/media/Files/chemicals/reviews/nair-fluopyram.ashx.
- ↑ "Durchführungsverordnung (EU) Nr. 802/2013 Der Kommission" (in German). August 2013. http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2013:225:0013:0016:DE:PDF.
 |
