Chemistry:Fosdenopterin
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Nulibry |
| Other names | Precursor Z, ALXN1101 |
| License data | |
| Routes of administration | Intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
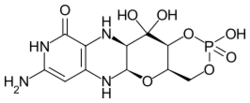
| Formula | C10H14N5O8P |
| Molar mass | 363.223 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Fosdenopterin (or cyclic pyranopterin monophosphate, cPMP), sold under the brand name Nulibry, is a medication used to reduce the risk of death due to a rare genetic disease known as molybdenum cofactor deficiency type A.[2]
The most common side effects include complications related to the intravenous line, fever, respiratory infections, vomiting, gastroenteritis, and diarrhea.[2]
Fosdenopterin was approved for medical use in the United States in February 2021,[4] It is the first medication approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of molybdenum cofactor deficiency type A.[2] and in the European Union in September 2022.[3] The US Food and Drug Administration considers it to be a first-in-class medication.[5]
Medical uses
Fosdenopterin is indicated to reduce the risk of mortality in people with molybdenum cofactor deficiency (MoCD) type A.[1][2]
Mechanism of action
People with molybdenum cofactor deficiency type A cannot produce cyclic pyranopterin monophosphate (cPMP) in their body.[2] Fosdenopterin is an intravenous medication that replaces the missing cPMP.[2][6] cPMP is a precursor to molybdopterin, which is required for the enzyme activity of sulfite oxidase, xanthine dehydrogenase/oxidase and aldehyde oxidase.[7]
History
Fosdenopterin was developed at the German universities TU Braunschweig and the University of Cologne.[8][9]
The effectiveness of fosdenopterin for the treatment of MoCD-A was demonstrated in thirteen treated participants compared to eighteen matched, untreated participants.[2][10] The participants treated with fosdenopterin had a survival rate of 84% at three years, compared to 55% for the untreated participants.[2]
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted the application for fosdenopterin priority review, breakthrough therapy, and orphan drug designations along with a rare pediatric disease priority review voucher.[2][5] The FDA granted the approval of Nulibry to Origin Biosciences, Inc., in February 2021.[2]
Society and culture
Legal status
On 21 July 2022, the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) of the European Medicines Agency (EMA) adopted a positive opinion, recommending the granting of a marketing authorization under exceptional circumstances for the medicinal product Nulibry, intended for the treatment of patients with molybdenum cofactor deficiency (MoCD) Type A.[11] The applicant for this medicinal product is Comharsa Life Sciences Ltd.[11] Fosdenopterin was approved for medical use in the European Union in September 2022.[3][12]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Nulibry- fosdenopterin hydrobromide injection, powder, for solution". https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=4f67cc4e-84ed-4f4e-a5d9-6ffbfb84eddd.
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 "FDA Approves First Treatment for Molybdenum Cofactor Deficiency Type A". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). 26 February 2021. Archived from the original on 27 February 2021. Retrieved 26 February 2021.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "Nulibry EPAR". 18 July 2022. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/nulibry. Text was copied from this source which is copyright European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged.
- ↑ "Drug Approval Package: Nulibry". 26 March 2021. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2021/214018Orig1s000TOC.cfm.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 (PDF) Advancing Health Through Innovation: New Drug Therapy Approvals 2021 (Report). 13 May 2022. https://www.fda.gov/media/155227/download. Retrieved 22 January 2023.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ DrugBank DB16628 . Accessed 5 March 2021.
- ↑ "The tetrahydropyranopterin structure of the sulfur-free and metal-free molybdenum cofactor precursor". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 279 (16): 15994–9. April 2004. doi:10.1074/jbc.M311815200. PMID 14761975.
- ↑ "Rescue of lethal molybdenum cofactor deficiency by a biosynthetic precursor from Escherichia coli". Human Molecular Genetics 13 (12): 1249–55. June 2004. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddh136. PMID 15115759.
- ↑ "Doctors risk untried drug to stop baby's brain dissolving". TimesOnline. 5 November 2009. https://www.thetimes.co.uk/article/doctors-risk-untried-drug-to-stop-babys-brain-dissolving-rbp08z32pwr.
- ↑ "Efficacy and safety of cyclic pyranopterin monophosphate substitution in severe molybdenum cofactor deficiency type A: a prospective cohort study". Lancet 386 (10007): 1955–63. November 2015. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00124-5. PMID 26343839.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 "Nulibry: Pending EC decision". 22 July 2022. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/summaries-opinion/nulibry. Text was copied from this source which is copyright European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged.
- ↑ "Nulibry Product information". https://ec.europa.eu/health/documents/community-register/html/h1684.htm.
External links
- "Fosdenopterin". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://druginfo.nlm.nih.gov/drugportal/name/fosdenopterin.
 |
