Chemistry:Fraxin
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
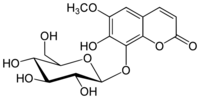
| IUPAC name
8-(β-D-Glucopyranosyloxy)-7-hydroxy-6-methoxy-2H-1-benzopyran-2-one
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
7-Hydroxy-6-methoxy-8-{[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy}-2H-1-benzopyran-2-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H18O10 | |
| Molar mass | 370.310 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Fraxin is a glucoside of fraxetin.[1] Fraxin extracted from ash bark exhibits florescence in aqueous solution.[2] A blue/green luminescence can be observed by soaking ash twigs in hot water.
Bibliography
- ↑ Hirsch, Anne-Marie; Longeon, Arlette; Guyot, Michèle (January 2002). "Fraxin and esculin: two coumarins specific to Actinidia chinensis and A. deliciosa (kiwifruit)" (in en). Biochemical Systematics and Ecology 30 (1): 55–60. doi:10.1016/S0305-1978(01)00064-3. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0305197801000643.
- ↑ Meikle, R. D. (1958) (in English). British Trees and Shrubs (Kew Series) (1st ed.). UK: Eyre & Spottiswoode. pp. 129-132.
 |
