Chemistry:Glycine N-carboxyanhydride
From HandWiki
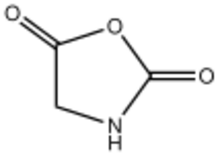
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,3-Oxazolidine-2,5-dione | |
| Other names
glycine N-carboxyanhydride
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H3NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 101.061 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Density | 1.74 g/cm3[1] |
| Melting point | 96–98[2] °C (205–208 °F; 369–371 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H315, H318, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P264+265Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P271, P280, P302+352, P304+340, P305+354+338Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P317Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P319Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P321, P332+317Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P362+364Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Glycine N-carboxyanhydride is an organic compound with the formula HNCH(CO)2O. A colorless solid, it is the product of phosgenation (reaction with phosgene) of glycine.[4][5] Glycine N-carboxyanhydride is the simplest member of the amino acid N-carboxyanhydrides. It is also the parent of the 2,5-oxazolidinedione family of heterocycles.
Other derivatives
2,5-Oxazolidinediones can also be prepared from Schiff base derivatives of amino acids.[6]
See also
- 2,4-Oxazolidinedione, parent ring found in a variety anticonvulsant drugs.
References
- ↑ Kanazawa, Hitoshi; Matsuura, Yoshiki; Tanaka, Nobuo; Kakudo, Masao; Komoto, Tadashi; Kawai, Tohru (1976). "The Crystal and Molecular Structure ofN-Carboxy Anhydride of Glycine". Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan 49 (4): 954–956. doi:10.1246/bcsj.49.954.
- ↑ Wilder, Renee; Mobashery, Shahriar (1992). "The use of triphosgene in preparation of N-carboxy .alpha.-amino acid anhydrides". The Journal of Organic Chemistry 57 (9): 2755–2756. doi:10.1021/jo00035a044.
- ↑ "Oxazolidine-2,5-dione" (in en). https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/75136#section=Safety-and-Hazards.
- ↑ "Polypeptides and 100 years of chemistry of alpha-amino acid N-carboxyanhydrides". Angewandte Chemie 45 (35): 5752–84. September 2006. doi:10.1002/anie.200600693. PMID 16948174.
- ↑ "A Moisture-Tolerant Route to Unprotected α/β-Amino Acid N-carboxyanhydrides and Facile Synthesis of Hyperbranched Polypeptides". Nature Communications 12 (1): 5810. October 2021. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-25689-y. PMID 34608139. Bibcode: 2021NatCo..12.5810T.
- ↑ "Direct synthesis of imidazolidin-4-ones via cycloadditions of imines with a Leuchs' anyhdride". Tetrahedron Letters 56 (20): 2590–2. 2015. doi:10.1016/j.tetlet.2015.04.002.
 |

