Chemistry:HEPBS
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
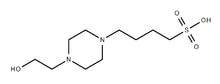
| Preferred IUPAC name
4-[4-(2-Hydroxyethyl)piperazin-1-yl]butane-1-sulfonic acid | |
| Other names
HEPBS
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H22N2O4S | |
| Molar mass | 266.356 g/mol |
| Appearance | White crystalline powder |
| Density | 1.25 g/cm3 (predicted) |
| Melting point | 211–216 °C (412–421 °F; 484–489 K) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 8.3 |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Irritant |
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
HEPBS (N-(2-Hydroxyethyl)piperazine-N'-(4-butanesulfonic acid)) is a zwitterionic organic chemical buffering agent; one of Good's buffers. HEPBS and HEPES have very similar structures and properties, HEPBS also having an acidity (pKa) in the physiological range (7.6-9.0 useful range). This makes it possible to use it for cell culture work.

References
 |
