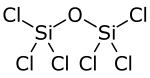
Chemistry:Hexachlorodisiloxane
From HandWiki
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Cl6OSi2 | |
| Molar mass | 284.87 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.575 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −33 °C (−27 °F; 240 K) |
| Boiling point | 137 °C (279 °F; 410 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H223, H314, H335 | |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Hexafluorodisiloxane |
Other cations
|
Perchloromethylether |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Hexachlorodisiloxane is a chemical compound composed of chlorine, silicon, and oxygen. Structurally, it is the symmetrical ether of two trichlorosilyl groups, and can be synthesized via high-temperature oxidation of silicon tetrachloride: [math]\ce{ 2SiCl4{} + O2 ->[\atop{950-970\,^\circ\text{C}}] 2(SiCl3)2O{} + Cl2 }[/math]
At room temperature, it is a colorless liquid that hydrolyzes upon exposure to water to give silicon dioxide and hydrochloric acid: [math]\ce{ (SiCl3)2O + 3H2O -> 2SiO2 + 6HCl }[/math] Intense heat evinces a similar decomposition: [math]\ce{ 2(SiCl3)2O ->[\atop{\Delta}] SiO2{} + 3SiCl4 }[/math]
Reaction with antimony trifluoride gives the analogous hexafluorodisiloxane.
Sources
- Lide, David R., ed (2009). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (90th ed.). Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-4200-9084-0.
- G. Brauer [Брауэр Г.], ed (1985) (in ru). 3. Moscow: Mir. p. 392.
- K. A. Adrianov [Адрианов К. А.] (1955) (in ru). Moscow: State scientific and technical publishing house of chemical literature. p. 521.
- Booth, Harold Simmons; Osten, Reuben Alexander (July 1945). "The Fluorination of Chlorodisiloxane / Silicon Oxyfluoride". Journal of the American Chemical Society 67 (7): 1092–1096. doi:10.1021/ja01223a021.
References
 |

