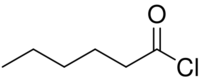
Chemistry:Hexanoyl chloride
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Hexanoyl chloride | |
| Other names
Caproyl chloride
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H11ClO | |
| Molar mass | 134.60 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Maybe toxic and corrosive |
| GHS pictograms |   
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H226, H302, H314, H335 | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+312, P301+330+331, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P312, P321, P330, P363, P370+378, P403+233, P403+235 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Hexanoyl chloride is a six-carbon acyl chloride with a straight-chain structure that is used as a reagent in organic synthesis.[1][2][3][4]
References
- ↑ "Hexanoyl chloride". Sigma-Aldrich. http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/aldrich/294659?lang=en®ion=US. Retrieved 1 July 2017.
- ↑ Jeremy P. E. Spencer; Alan Crozier (24 April 2012). Flavonoids and Related Compounds: Bioavailability and Function. CRC Press. pp. 263–4. ISBN 978-1-4398-4827-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=30DNBQAAQBAJ&pg=PA263.
- ↑ Vijay Kumar Thakur; Amar Singh Singha (27 April 2015). Surface Modification of Biopolymers. John Wiley & Sons. p. 265. ISBN 978-1-118-66955-6. https://books.google.com/books?id=jWJvCAAAQBAJ&pg=PA265.
- ↑ Robert Martin; Jean-Pierre Buisson (24 February 2015). Aromatic Hydroxyketones: Preparation & Physical Properties: Aromatic Hydroxyketones from Butanone (C4) to Dotriacontanone (C32). Springer. pp. 661 etc.. ISBN 978-3-319-14185-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=fu_LBgAAQBAJ&pg=PA661.
 |

