Chemistry:Hexaphenylbenzene
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
23,24,25,26-Tetraphenyl-11,21:22,31-terphenyl | |
| Other names
Hexaphenylbenzene
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C42H30 | |
| Molar mass | 534.702 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Melting point | 454 to 456 °C (849 to 853 °F; 727 to 729 K)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
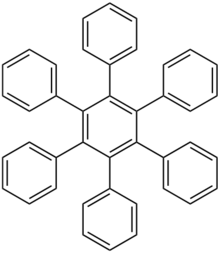
Hexaphenylbenzene is an aromatic compound composed of a benzene ring substituted with six phenyl rings. It is a colorless solid. The compound is the parent member of a wider class of hexaarylbenzenes, which are mainly of theoretical interest.[2]
Preparation
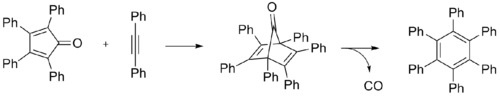
It is prepared by heating tetraphenylcyclopentadienone and diphenylacetylene in benzophenone or other high-temperature solvent. The reaction proceeds via a Diels-Alder reaction to give the hexaphenyldienone, which then eliminates carbon monoxide.[1]
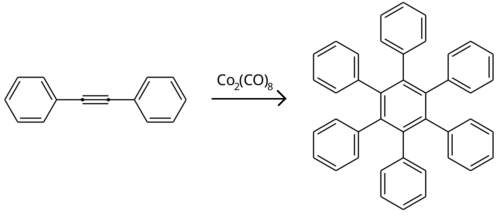
Together with 1,2,3,4-tetraphenylnaphthalene, hexaphenylbenzene forms by the chromium-catalyzed oligomerization of diphenylacetylene.[3] It may also be prepared by the dicobalt octacarbonyl-catalyzed alkyne trimerisation of diphenylacetylene.[2]
Structure
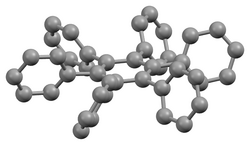
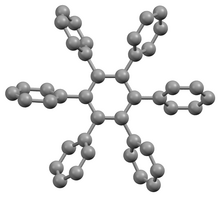
The stable conformation of this molecule has the phenyl rings rotated out of the plane of the central benzene ring. The molecule adopts a propeller-like conformation in which the phenyl rings are rotated about 65°,[4] while in the gas phase, they are perpendicular with some slight oscillations.[5]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Louis Fieser (1966). "Hexaphenylbenzene". Organic Syntheses 46: 44. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.046.0044.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Varun Vij, Vandana Bhalla, and Manoj Kumar (2016). "Hexaarylbenzene: Evolution of Properties and Applications of Multitalented Scaffold". Chemical Reviews 116 (16): 9565–9627. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00144. PMID 27498592.
- ↑ W. Herwig, W. Metlesics, H. Zeiss (1959). "π-Complexes of the Transition Metals. X. Acetylenic π-Complexes of Chromium in Organic Synthesis". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 81 (23): 6203–6207. doi:10.1021/ja01532a024.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Bart, J. C. J. (1968). "The crystal structure of a modification of hexaphenylbenzene". Acta Crystallographica Section B 24 (10): 1277–1287. doi:10.1107/S0567740868004176. http://journals.iucr.org/b/issues/1968/10/00/a06258/a06258.pdf.[yes|permanent dead link|dead link}}]
- ↑ Gust, D. (1977). "Restricted Rotation in Hexaarylbenzenes". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 99 (21): 6980–6982. doi:10.1021/ja00463a034.
 |