Chemistry:Hollandite
| Hollandite | |
|---|---|
 | |
| General | |
| Category | Oxide minerals |
| Formula (repeating unit) | Ba(Mn4+6Mn3+2)O16 |
| Strunz classification | 4.DK.05a |
| Dana classification | 7.9.1.1 |
| Crystal system | Monoclinic |
| Crystal class | Prismatic (2/m) |
| Space group | Monoclinic H-M symbol: (2/m) Space group: I2/m |
| Identification | |
| Color | Silvery-grey to greyish |
| Cleavage | Distinct / Good, Prismatic |
| Mohs scale hardness | 4 to 6 |
| Density | 4.95[1] |
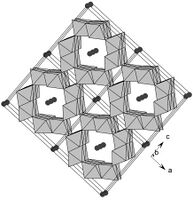
Hollandite (chemical formula: Ba(Mn4+6Mn3+2)O16) is a manganese oxide mineral.[1] Its structure consists of double chains of MnO6 octahedra delimiting 2 × 2 tunnels. The electrostatic charge created by the Mn3+ for Mn4+ substitution is balanced by cations in the tunnels. Their nature determines the mineral species: Ba for hollandite, K for cryptomelane, Pb for coronadite, Sr for strontiomelane,[3] Tl for thalliomelane,[4] and Na for manjiroite.[5] Pure species are rare and most 2 × 2 tectomanganates contain mixtures of several types of tunnel cations.
A mineral, with the chemical composition BaMn4+6Fe3+2O16,[6] that was first found in the Kajlidongri mine in the Jhabua district of Madhya Pradesh, India,[7] had the name hollandite until it was reclassified as ferrihollandite by the International Mineralogical Association in 2012. Ferrihollandite is the barium-iron (III) endmember of the coronadite group.[1]
Polyhedral representation of the 2 x 2 tunnel structure of hollandite. The black atoms represent Ba.[8]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "Hollandite". https://www.mindat.org/min-1921.html.
- ↑ Warr, L.N. (2021). "IMA–CNMNC approved mineral symbols". Mineralogical Magazine 85 (3): 291–320. doi:10.1180/mgm.2021.43. Bibcode: 2021MinM...85..291W.
- ↑ Mindat.org
- ↑ Mindat.org
- ↑ Mindat.org
- ↑ "Archived copy". http://ima-cnmnc.nrm.se/.
- ↑ "Hollandite". p. 252. http://rruff.info/doclib/hom/hollandite.pdf.
- ↑ Post JE, Von Dreele RB, Buseck P (1982) Acta Crystallographica B38: 1056-1065
 |