Chemistry:Iminoborane
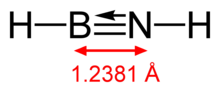 Iminoborane (parent compound)
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Boraneimine
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| BH2N | |
| Molar mass | 26.83 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Iminoboranes comprise a group of organoboron compounds with the formula RB=NR'. They are electronically related to acetylenes but are usually more reactive due to the polarity.[2][3]
Structure and bonding
The parent iminoborane, HB=NH, is produced by the photolysis of H3BNH3.[4][5][6] Bonding in iminoboranes can be described by two resonance structures:[7]
- [math]\ce{ R-\overset{\ominus}{B}{\equiv}\overset{\oplus}{N}-R <-> R-B=\ddot{N}-R }[/math]
The stability is dramatically affected by bulky substituents. One isolable iminoborane is (CH
3)
3C–B−
≡N+
–C(CH
3)
3.[1]
| Molecule | Ammonia borane[8] | Aminoborane[9] | Iminoborane[10] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Formula | BNH6 | BNH4 | BNH2 |
| Class | amine-borane | aminoborane | iminoborane |
| Analogous hydrocarbon | ethane | ethylene | acetylene |
| Analogous hydrocarbon class | alkane | alkene | alkyne |
| Structure | 
| ||
| Ball-and-stick model | 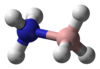
|
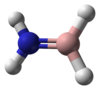
|
|
| Hybridisation of boron and nitrogen | sp3 | sp2 | sp |
| B-N bond length | 1.658 Å | 1.391 Å | 1.238 Å |
| Proportion of B-N single bond | 100% | 84% | 75% |
| B-H bond length | 1.216 Å | 1.195 Å | |
| N-H bond length | 1.014 Å | 1.004 Å | |
| Structure determination method | microwave spectroscopy | microwave spectroscopy | infrared spectroscopy |
Synthesis
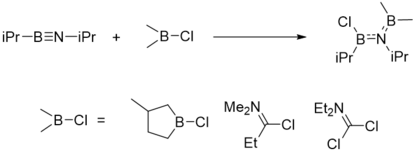
Elimination of fluoro- or chlorosilanes provides a well-tested route. Bulky substituents such as (Me3Si)3Si stabilize the iminoborane with respect to oligomerization:[11]
- (Me3Si)3SiB(F)-N(SiMe3)2 → (Me3Si)3Si-B=N-SiMe3 + F-SiMe3
Thermal decomposition of azidoboranes induces migration of R from boron to the nascent nitrene gives iminoboranes:[12]
- R2B-N3 → RB=NR + N2
Reactivity
Oligomerization
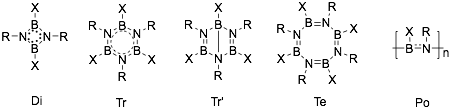
Iminoboranes tend to oligomerize, often forming cyclic derivatives. Preventing this reaction is the purpose of bulky substituents. Five types of oligomerization product are produced: cyclodimers (1,3-diaza-2,4-diboretidines,[1] Di[13]), cyclotrimers (borazines, Tr), bicyclotrimers (Dewar borazines, Tr′[14]), cyclotetramers (octahydro-1,3,5,7-tetraza-2,4,6,8-tetraborocines, Te[15]), and polymers (polyiminoboranes, Po); which are shown below.[16] Which product is dominant depends on the structures of reactants and the reaction conditions. Some of the products can be interconverted.[17]
Addition reactions
The addition of protic agents is fast and quantitive.[18] Boration reaction of iminoboranes is the addition of B-X single bond to B≡N, where -X can be -Cl (chloro-boration), -N3 (azido-boration), -SR (thio-boration), -NR2 (amino-boration) and R (alkyl-boration). One of these reactions are illustrated here.
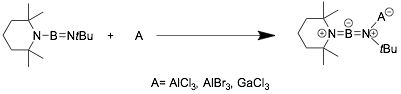
Some electron-rich iminoboranes form adducts with Lewis acids.[19]
Cycloaddition
The typical [2+3]-cycloaddition is the addition of B≡N and RN3 to give a BN4 ring.[1] One of the widely investigated [2+2]-cycloadditions is the reaction of aldehydes and ketones.
Coordination to transition metals
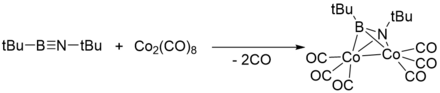
Like alkynes, iminoboranes bind transition metals.
References
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Paetzold, Peter; Plotho, Christoph Von; Schmid, Günter; Boese, Roland; Schrader, Bernhard; Bougeard, Daniel; Pfeiffer, Uwe; Gleiter, Rolf et al. (1984). "Darstellung, Reaktionen und Struktur vontert-Butyl(tert-butylimino)boran". Chemische Berichte 117 (3): 1089–1102. doi:10.1002/cber.19841170324.
- ↑ Inorganic ring systems : 7th International symposium : Papers.. Chivers, Tristram. Gordon and Breach Science Publishers. 1994. ISBN 978-2-88449-168-6. OCLC 81135356.
- ↑ Paetzold, Peter (1987) (in en). Iminoboranes. Advances in Inorganic Chemistry. 31. pp. 123–170. doi:10.1016/s0898-8838(08)60223-8. ISBN 978-0-12-023631-2. https://archive.org/details/trent_0116400835595_31/page/123.
- ↑ Lory, Earl R.; Porter, Richard F. (1973-03-01). "Infrared studies of matrix isolated species in the hydrogen-boron-nitrogen system". Journal of the American Chemical Society 95 (6): 1766–1770. doi:10.1021/ja00787a012. ISSN 0002-7863.
- ↑ Paetzold, Peter; Richter, Anette; Thijssen, Theo; Würtenberg, Stefan (1979-12-01). "Bildung, Struktur und Reaktivität von (Pentafluorphenyl)bor-tert-butylimid und seinem Cyclodimeren" (in en). Chemische Berichte 112 (12): 3811–3827. doi:10.1002/cber.19791121207. ISSN 1099-0682.
- ↑ Paetzold, Peter; von Plotho, Christoph (1982-08-01). "Über weitere monomere Borimide und ihre Reaktionen" (in en). Chemische Berichte 115 (8): 2819–2825. doi:10.1002/cber.19821150813. ISSN 1099-0682.
- ↑ Mó, Otilia; Yáñez, Manuel; Pendás, Angel Martín; Bene, Janet E. Del; Alkorta, Ibon; Elguero, José (2007-07-23). "Unusual substituent effects on the bonding of iminoboranes" (in en). Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 9 (30): 3970–3977. doi:10.1039/b702480k. ISSN 1463-9084. PMID 17646885. Bibcode: 2007PCCP....9.3970M. http://xlink.rsc.org/?DOI=B702480K.
- ↑ Thorne, L. R.; Suenram, R. D.; Lovas, F. J. (1983). "Microwave spectrum, torsional barrier, and structure of BH3NH3". J. Chem. Phys. 78 (1): 167–171. doi:10.1063/1.444528. Bibcode: 1983JChPh..78..167T.
- ↑ Sugie, Masaaki; Takeo, Harutoshi; Matsumura, Chi (1987). "Microwave spectrum and molecular structure of aminoborane, BH2NH2". J. Mol. Spectrosc. 123 (2): 286–292. doi:10.1016/0022-2852(87)90279-7. Bibcode: 1987JMoSp.123..286S.
- ↑ Kawashima, Yoshiyuki (1987). "Detection of HBNH by infrared diode laser spectroscopy". J. Chem. Phys. 87 (11): 6331–6333. doi:10.1063/1.453462. Bibcode: 1987JChPh..87.6331K.
- ↑ Haase, Martin; Klingebiel, Uwe (1985-04-01). "Simple Synthesis of Stable Iminoboranes" (in en). Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English 24 (4): 324. doi:10.1002/anie.198503241. ISSN 1521-3773.
- ↑ Paetzold, Peter; Eleftheriadis, Eleftherios; Minkwitz, Rolf; Wölfel, Volker; Gleiter, Rolf; Bischof, Peter; Friedrich, Gert (1988-01-01). "Bildung, Struktur und Reaktionen von Methyl(methylimino)boran" (in en). Chemische Berichte 121 (1): 61–66. doi:10.1002/cber.19881210110. ISSN 1099-0682.
- ↑ Hess, H. (1969-11-15). "Strukturbestimmungen an Bor–Stickstoff-Verbindungen. IV. Die Kristall- und Molekularstruktur von Hexakis(trimethylsilyl)-2,4-diamino-1,3,2,4-diazadiboretidin" (in de). Acta Crystallographica Section B 25 (11): 2342–2349. doi:10.1107/s056774086900567x. ISSN 0567-7408. http://journals.iucr.org/b/issues/1969/11/00/a06979/a06979.pdf.
- ↑ Steuer, Holger-A.; Meller, Anton; Elter, Gernot (1985). "B-t-butyl-borazine und -diazadiboretidine" (in de). Journal of Organometallic Chemistry 295 (1): 1–6. doi:10.1016/0022-328x(85)88065-7.
- ↑ Turner H. S. and Warne R. J. 1962 Proc. Chem. Soc. 69.
- ↑ Advances in inorganic chemistry. Volume 31. Emeléus, H. J. (Harry Julius), Sharpe, A. G.. New York: Academic Press. 1987. ISBN 978-0-12-023631-2. OCLC 277086713. https://archive.org/details/trent_0116400835595_31.
- ↑ Maier.G. (1978). "Tetra-tert-butyltetrahedrane". Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 17 (7): 520–521. doi:10.1002/anie.197805201.
- ↑ Nöth, Heinrich; Weber, Siegfried (1985-05-01). "Beiträge zur Chemie des Bors, 154. Addition von Trimethylsily-Verbindungen und von anderen Elektrophilen an (tert-Butylimino) (tetramethylpiperidino)boran" (in en). Chemische Berichte 118 (5): 2144–2146. doi:10.1002/cber.19851180536. ISSN 1099-0682.
- ↑ Nöth, Heinrich; Weber, Siegfried (1985-06-01). "Beiträge zur Chemie des Bors, 158. Addukte von Aluminium- und Galliumhalogeniden an ein Aminoiminoboran" (in en). Chemische Berichte 118 (6): 2554–2556. doi:10.1002/cber.19851180631. ISSN 1099-0682.
 |