Chemistry:Ammonia borane
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Ammoniotrihydroborate
| |
| Other names | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| H 3NBH 3 | |
| Molar mass | 30.87 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless crystals |
| Density | 0.78 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 104 °C (219 °F; 377 K) |
| Structure | |
| I4mm, tetragonal | |
| Tetragonal at B and N | |
| Tetrahedral at B and N | |
| 5.2 D | |
| Hazards[4] | |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| HH228Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, HH302Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, HH315Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, HH319Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, HH332Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, HH335Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors | |
| PP210Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP240Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP241Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP261Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP264Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP264+P265Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP270Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP271Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP280Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP301+P317Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP302+P352Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP304+P340Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP305+P351+P338Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP317Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP319Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP321Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP330Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP332+P317Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP337+P317Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP362+P364Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP370+P378Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP403+P233Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP405Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP501Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors | |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
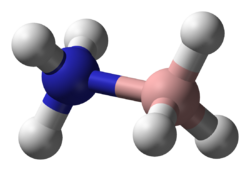
Ammonia borane (also systematically named ammoniotrihydroborate[citation needed]), also called borazane, is the chemical compound with the formula H
3NBH
3. The colourless or white solid is the simplest molecular boron-nitrogen-hydride compound. It has attracted attention as a source of hydrogen fuel, but is otherwise primarily of academic interest.
Synthesis
Reaction of diborane with ammonia mainly gives the diammoniate salt [H
2B(NH
3)
2]+
[BH
4]−
(diammoniodihydroboronium tetrahydroborate). Ammonia borane is the main product when an adduct of borane is employed in place of diborane:[5]
- BH
3(THF) + NH
3 → BH
3NH
3 + THF
It can also be synthesized from sodium borohydride.[6][7][8]
Properties and structure
The molecule adopts a structure similar to that of ethane, with which it is isoelectronic. The B−N distance is 1.58(2) Å. The B−H and N−H distances are 1.15 and 0.96 Å, respectively. Its similarity to ethane is tenuous since ammonia borane is a solid and ethane is a gas: their melting points differing by 284 °C. This difference is consistent with the highly polar nature of ammonia borane. The H atoms attached to boron are hydridic (negatively charged) and those attached to nitrogen are acidic (positively charged).[9]
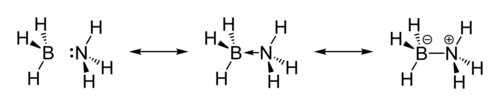
The structure of the solid indicates a close association of the NH and the BH centers. The closest H−H distance is 1.990 Å, which can be compared with the H−H bonding distance of 0.74 Å. This interaction is called a dihydrogen bond.[10][11] The original crystallographic analysis of this compound reversed the assignments of B and N. The updated structure was arrived at with improved data using the technique of neutron diffraction that allowed the hydrogen atoms to be located with greater precision.
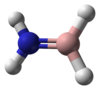
| Molecule | Ammonia borane[12] | Aminoborane[13] | Iminoborane[14] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Formula | BNH 6 |
BNH 4 |
BNH 2 |
| Class | amine-borane | aminoborane | iminoborane |
| Analogous hydrocarbon | ethane | ethylene | acetylene |
| Analogous hydrocarbon class | alkane | alkene | alkyne |
| Structure | 
| ||
| Ball-and-stick model | 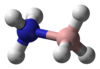
|
|
|
| Hybridisation of boron and nitrogen | sp3 | sp2 | sp |
| B-N bond length | 1.658 Å | 1.391 Å | 1.238 Å |
| Proportion of B-N single bond | 100% | 84% | 75% |
| Structure determination method | microwave spectroscopy | microwave spectroscopy | infrared spectroscopy |
Uses
Ammonia borane has been suggested as a storage medium for hydrogen, e.g. for when the gas is used to fuel motor vehicles. It can be made to release hydrogen on heating, being polymerized first to (NH
2BH
2)
n, then to (NHBH)
n,[15] which ultimately decomposes to boron nitride (BN) at temperatures above 1000 °C.[16] It is more hydrogen-dense than liquid hydrogen and also able to exist at normal temperatures and pressures.[17]
Ammonia borane finds some use in organic synthesis as an air-stable derivative of diborane.[18] It can be used as a reducing agent in transfer hydrogenation reactions, often in the presence of a transition metal catalyst.[19]
Analogous amine-boranes
Many analogues have been prepared from primary, secondary, and even tertiary amines:
- Borane tert-butylamine ((CH
3)
3C–NH
2→BH
3) - Borane trimethylamine ((CH
3)
3N→BH
3) - Borane isopropylamine ((CH
3)
2CH–NH
2→BH
3)
The first amine adduct of borane was derived from trimethylamine. Borane tert-butylamine complex is prepared by the reaction of sodium borohydride with t-butylammonium chloride. Generally adduct are more robust with more basic amines. Variations are also possible for the boron component, although primary and secondary boranes are less common.[8]
See also
- Phosphine-borane (R
3P→BH
3) - borane dimethylsulfide ((CH
3)
2S→BH
3) - borane–tetrahydrofuran (THF→BH
3)
References
- ↑ https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2015177483A1/en
- ↑ Umemoto, Hironobu; Miyata, Atsushi (2015). "Decomposition processes of diborane and borazane (ammonia-borane complex) on hot wire surfaces". Thin Solid Films. 8th International conference on hot-wire CVD (Cat-CVD) processes (HWCVD 8) 595: 231–234. doi:10.1016/j.tsf.2015.04.084. Bibcode: 2015TSF...595..231U.
- ↑ https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/GB/en/search/borazane?focus=products&page=1&perpage=30&sort=relevance&term=borazane&type=product
- ↑ https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Ammonia-borane
- ↑ Shore, S. G.; Boddeker, K. W. (1964). "Large Scale Synthesis of H2B(NH3)2+BH4− and H3NBH3". Inorganic Chemistry 3 (6): 914–915. doi:10.1021/ic50016a038.
- ↑ Hu, M.G.; Van Paasschen, J.M.; Geanangel, R.A. (January 1977). "New synthetic approaches to ammonia-borane and its deuterated derivatives". Journal of Inorganic and Nuclear Chemistry 39 (12): 2147–2150. doi:10.1016/0022-1902(77)80383-7.
- ↑ Ramachandran, P. Veeraraghavan; Mistry, Hitesh; Kulkarni, Ameya S.; Gagare, Pravin D. (2014). "Ammonia-mediated, large-scale synthesis of ammonia borane". Dalton Trans. 43 (44): 16580–16583. doi:10.1039/C4DT02467B. PMID 25274135.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Staubitz, Anne; Robertson, Alasdair P. M.; Manners, Ian (2010). "Ammonia-Borane and Related Compounds as Dihydrogen Sources". Chemical Reviews 110 (7): 4079–4124. doi:10.1021/cr100088b. PMID 20672860.
- ↑ Bowden, Mark E.; Gainsford, Graeme J.; Robinson, Ward T. (2007). "Room-Temperature Structure of Ammonia Borane". Australian Journal of Chemistry 60 (3): 149. doi:10.1071/ch06442. ISSN 0004-9425.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Klooster, W. T.; Koetzle, T. F.; Siegbahn, P. E. M.; Richardson, T. B.; Crabtree, R. H. (1999). "Study of the N−H···H−B Dihydrogen Bond Including the Crystal Structure of BH3NH3 by Neutron Diffraction". Journal of the American Chemical Society 121 (27): 6337–6343. doi:10.1021/ja9825332.
- ↑ Boese, R.; Niederprüm, N.; Bläser, D. (1992). Maksic, Z. B.. ed. Molecules in Natural Science and Medicine. Chichester, England: Ellis Horwood. ISBN 978-0135615980.
- ↑ Thorne, L. R.; Suenram, R. D.; Lovas, F. J. (1983). "Microwave spectrum, torsional barrier, and structure of BH3NH3". J. Chem. Phys. 78 (1): 167–171. doi:10.1063/1.444528. Bibcode: 1983JChPh..78..167T.
- ↑ Sugie, Masaaki; Takeo, Harutoshi; Matsumura, Chi (1987). "Microwave spectrum and molecular structure of aminoborane, BH2NH2". J. Mol. Spectrosc. 123 (2): 286–292. doi:10.1016/0022-2852(87)90279-7. Bibcode: 1987JMoSp.123..286S.
- ↑ Kawashima, Yoshiyuki (1987). "Detection of HBNH by infrared diode laser spectroscopy". J. Chem. Phys. 87 (11): 6331–6333. doi:10.1063/1.453462. Bibcode: 1987JChPh..87.6331K.
- ↑ Gutowski, M.; Autrey, T. (2006). "Features: Hydrogen gets onboard". Chemistry World 3 (3). http://www.rsc.org/chemistryworld/Issues/2006/March/HydrogenOnBoard.asp.
- ↑ Frueh, S.; Kellett, R.; Mallery, C.; Molter; T.; Willis, W. S.; King'ondu, C.; Suib, S. L. (2011). "Pyrolytic Decomposition of Ammonia Borane to Boron Nitride". Inorganic Chemistry 50 (3): 783–792. doi:10.1021/ic101020k. PMID 21182274.
- ↑ Stephens, F. H.; Pons, V.; Baker, R. T. (2007). "Ammonia–Borane: The Hydrogen Source par excellence?". Dalton Transactions 2007 (25): 2613–2626. doi:10.1039/b703053c. PMID 17576485.
- ↑ Andrews, Glenn C.; Neelamkavil, Santhosh F. (2008). "Borane–Ammonia". in Paquette, Leo A.. Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. New York City: John Wiley & Sons. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rb238.pub2. ISBN 978-0471936237.
- ↑ Zhao, Wenfeng; Li, Hu; Zhang, Heng; Yang, Song; Riisager, Anders (August 2023). "Ammonia borane-enabled hydrogen transfer processes: Insights into catalytic strategies and mechanisms". Green Energy & Environment 8 (4): 948–971. doi:10.1016/j.gee.2022.03.011. Bibcode: 2023GrEE....8..948Z.
 |
![Part of the crystal structure of ammonia borane[10]](/wiki/images/thumb/9/93/Ammonia-borane-xtal-3D-balls.png/300px-Ammonia-borane-xtal-3D-balls.png)

