Chemistry:Indenol
From HandWiki
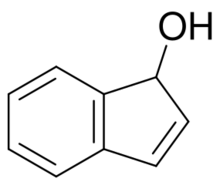 Chemical structure of 1-indenol
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H8O | |
| Molar mass | 132.162 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Indenols are hydroxylated indene. 3-Indenol is an enol forms of 1-indanone, and 2-indenol is an enol form of 2-indanone. Isomerization of 1-indenol can produce 1-indanone.[1] Indenolol is a derivative of a phenolic indenol.[2]
References
- ↑ "Conversion of indene to cis -(1 S ),(2 R )-indandiol by mutants of Pseudomonas putida F1". Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology 18 (6): 353–359. 1997. doi:10.1038/sj.jim.2900402.
- ↑ "Indenolol: a new antihypertensive agent: efficacy, toxicity, and hemodynamic effects in a crossover double-blind study with metoprolol". Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 25 (5): 328–36. 1985. doi:10.1002/j.1552-4604.1985.tb02850.x. PMID 4031109.
 |

