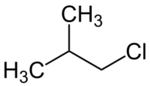
Chemistry:Isobutyl chloride
From HandWiki
|
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-Chloro-2-methylpropane | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 635650 | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1127 | ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C4H9Cl | |||
| Molar mass | 92.57 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colourless liquid | ||
| Density | 877 mg mL−1 | ||
| Melting point | −131 °C (−204 °F; 142 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 68.3 to 69.3 °C; 154.8 to 156.7 °F; 341.4 to 342.4 K | ||
| log P | 2.486 | ||
Henry's law
constant (kH) |
630 nmol Pa−1 kg−1 | ||
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.398 | ||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Heat capacity (C)
|
158.6 J K−1 mol−1 | ||
Std enthalpy of
combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
−2.7012–−2.6844 MJ mol−1 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS pictograms | 
| ||
| GHS Signal word | DANGER | ||
| H225 | |||
| P210 | |||
| Flash point | −19.4 °C (−2.9 °F; 253.8 K) | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related alkanes
|
2-bromo-1-chloropropane | ||
Related compounds
|
2-chloroethanol | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Tracking categories (test):
Isobutyl chloride (1-chloro-2-methylpropane) is an organochlorine compound. It is a chlorinated derivative of isobutane.
Synthesis
Isobutyl chloride can be synthesized in a substitution reaction by reacting isobutanol with hydrochloric acid:
- [math]\ce{ (CH3)2CH-CH2-OH\ +\ HCl -> [\ce{H2SO4}_\text{(conc)}] (CH3)2CH-CH2-Cl }[/math]
References
- ↑ "ISOBUTYL CHLORIDE - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 27 March 2005. Identification. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/summary/summary.cgi?cid=10554&loc=ec_rcs. Retrieved 25 June 2012.
 |