Chemistry:Isobutyryl chloride
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Methylpropanoyl chloride | |
| Other names
Isobutyroyl chloride
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H7ClO | |
| Molar mass | 106.55 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.017 g/mL[1] |
| Melting point | −90 °C [1] |
| Boiling point | 91–93 °C (196–199 °F; 364–366 K)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
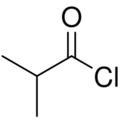
Isobutyryl chloride (2-methylpropanoyl chloride) is the organic compound with the formula (CH
3)
2CHCOCl. A colorless liquid, it the simplest branched-chain acyl chloride. It is prepared by chlorination of isobutyric acid.[2]
Reactions
As an ordinary acid chloride, isobutyryl chloride is the subject of many reported transformations. Dehydrohalogenation of isobutyryl chloride with triethylamine gives 2,2,4,4-tetramethylcyclobutanedione.[3] Treatment of isobutyryl chloride with hydrogen fluoride gives the acid fluoride.[4]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "Isobutyryl chloride". Sigma-Aldrich. https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/aldrich/139122?lang=en.
- ↑ Kent, R. E.; McElvain, S. M. (1945). "Isobutyramide". Organic Syntheses 25: 58. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.025.0058.
- ↑ R. Huisgen, P. Otto (1968), "The mechanism of dimerization of dimethylketene", J. Am. Chem. Soc. 90 (19): 5342–5343, doi:10.1021/ja01021a090
- ↑ Olah, George A.; Kuhn, Stephen J. (1965). "Benzoyl Fluoride". Organic Syntheses 45: 3. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.045.0003.
 |

