Chemistry:L-733,060
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
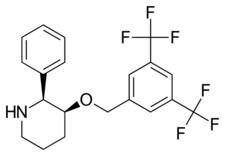
| Formula | C20H19F6NO |
| Molar mass | 403.368 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
L-733,060 is a drug developed by Merck which acts as an orally active, non-peptide, selective antagonist for the NK1 receptor, binding with a Ki of 0.08 nM.[1] Only one enantiomer is active which has made it the subject of several asymmetric synthesis efforts.[2][3][4]
L-733,060 has antidepressant[5][6] and anxiolytic effects in animal studies,[7] and reduces both the dopamine release and neurotoxicity produced by methamphetamine and cocaine.[8][9][10][11][12] It shows anti-inflammatory and anti-hepatotoxic effects in animals,[13][14] and counteracts the development of hyperalgesia following nerve injury.[15][16] It also has anticancer effects in a variety of in vitro models.[17][18][19]
See also
- NK1 receptor antagonists
- Aprepitant
- Casopitant
- Fosaprepitant
- Maropitant
- Vestipitant
- Vofopitant
References
- ↑ "L-733,060, a novel tachykinin NK1 receptor antagonist; effects in [Ca2+]i mobilisation, cardiovascular and dural extravasation assays". European Journal of Pharmacology 317 (1): 129–35. December 1996. doi:10.1016/S0014-2999(96)00706-6. PMID 8982729.
- ↑ "A general approach to (5S,6R)-6-alkyl-5-benzyloxy-2-piperidinones: application to the asymmetric syntheses of neurokinin substance P receptor antagonist (-)-L-733,061 and (-)-deoxocassine". The Journal of Organic Chemistry 69 (18): 6001–9. September 2004. doi:10.1021/jo049166z. PMID 15373484.
- ↑ "A novel and highly regioselective approach to 5-methoxy-6-substituted-3-sulfonyl-delta-enlactams from 5-methoxy-3-sulfonyl glutarimide: synthesis of cis-2-substituted-3-piperidinols". The Journal of Organic Chemistry 70 (5): 1780–5. March 2005. doi:10.1021/jo048073e. PMID 15730301.
- ↑ "Concise asymmetric synthesis of (+)-CP-99,994 and (+)-L-733,060 via efficient construction of homochiral syn-1,2-diamines and syn-1,2-amino alcohols". The Journal of Organic Chemistry 73 (8): 3307–10. April 2008. doi:10.1021/jo8002979. PMID 18331063.
- ↑ "The antidepressant-like effects of neurokinin NK1 receptor antagonists in a gerbil tail suspension test". Behavioural Pharmacology 14 (1): 87–95. February 2003. doi:10.1097/00008877-200302000-00009. PMID 12576885.
- ↑ "Behavioral and pharmacological validation of the gerbil forced-swim test: effects of neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists". Neuropsychopharmacology 33 (8): 1919–28. July 2008. doi:10.1038/sj.npp.1301586. PMID 17912250.
- ↑ "The gerbil elevated plus-maze II: anxiolytic-like effects of selective neurokinin NK1 receptor antagonists". Neuropsychopharmacology 27 (3): 371–9. September 2002. doi:10.1016/S0893-133X(02)00313-5. PMID 12225694.
- ↑ "Substance P modulates cocaine-evoked dopamine overflow in the striatum of the rat brain". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 937 (1): 121–31. June 2001. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2001.tb03561.x. PMID 11458533. Bibcode: 2001NYASA.937..121K.
- ↑ "Ontogeny of neurokinin-1 receptor mediation of methamphetamine neurotoxicity in the striatum of the mouse brain". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 965 (1): 247–53. June 2002. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2002.tb04166.x. PMID 12105100. Bibcode: 2002NYASA.965..247Y.
- ↑ "Neurokinin receptors modulate the neurochemical actions of cocaine". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 965 (1): 267–73. June 2002. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2002.tb04168.x. PMID 12105102. Bibcode: 2002NYASA.965..267N.
- ↑ "Neurokinin-1 (NK-1) receptor antagonists abrogate methamphetamine-induced striatal dopaminergic neurotoxicity in the murine brain". Journal of Neurochemistry 83 (3): 613–22. November 2002. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2002.01155.x. PMID 12390523.
- ↑ "Substance P and cholecystokinin regulate neurochemical responses to cocaine and methamphetamine in the striatum". Life Sciences 73 (6): 727–39. June 2003. doi:10.1016/S0024-3205(03)00393-X. PMID 12801594.
- ↑ "Neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists CP-96,345 and L-733,060 protect mice from cytokine-mediated liver injury". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 305 (1): 31–9. April 2003. doi:10.1124/jpet.102.043539. PMID 12649350.
- ↑ "Neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists protect mice from CD95- and tumor necrosis factor-alpha-mediated apoptotic liver damage". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 308 (3): 1174–80. March 2004. doi:10.1124/jpet.103.059329. PMID 14617692.
- ↑ "Involvement of peripherally released substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide in mediating mechanical hyperalgesia in a traumatic neuropathy model of the rat". Neuroscience Letters 360 (3): 129–32. April 2004. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2004.02.043. PMID 15082150.
- ↑ "Neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists inhibit the recruitment of opioid-containing leukocytes and impair peripheral antinociception". Anesthesiology 107 (6): 1009–17. December 2007. doi:10.1097/01.anes.0000291454.90754.de. PMID 18043070.
- ↑ "Neurokinin-1 receptors located in human retinoblastoma cell lines: antitumor action of its antagonist, L-732,138". Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science 48 (6): 2775–81. June 2007. doi:10.1167/iovs.05-1591. PMID 17525212.
- ↑ "NK-1 receptor antagonists induce apoptosis and counteract substance P-related mitogenesis in human laryngeal cancer cell line HEp-2". Investigational New Drugs 26 (2): 111–8. April 2008. doi:10.1007/s10637-007-9087-y. PMID 17906845.
- ↑ "The NK-1 receptor is expressed in human primary gastric and colon adenocarcinomas and is involved in the antitumor action of L-733,060 and the mitogenic action of substance P on human gastrointestinal cancer cell lines". Tumour Biology 29 (4): 245–54. 2008. doi:10.1159/000152942. PMID 18781096.
 |

