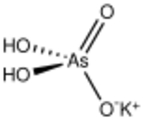
Chemistry:Monopotassium arsenate
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Potassium dihydrogen arsorate
| |
| Other names
Macquer's salt
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1677 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| AsH2KO4 | |
| Molar mass | 180.032 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Density | 2.867 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 288 °C (550 °F; 561 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |   
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H301, H331, H350, H410 | |
| P201, P202, P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P281, P301+310, P304+340, P308+313, P311, P321, P330, P391, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Monopotassium arsenate is the inorganic compound with the formula KH2AsO4. A white solid, this salt is used to prepared other arsenic-containing compounds, mainly pesticides. It is prepared by calcining arsenic oxide and potassium nitrate, followed by extraction with water.[1]
Relevant acid-base equilibria for aqueous solutions of this diprotic acid derived from arsenic acid are as follows:
- H3AsO4 + H2O ⇌ H2AsO−4 + H3O+ (pKa1 = 2.19)
- H2AsO−4 + H2O ⇌ HAsO2−4 + H3O+ (pKa2 = 6.94)
Related compounds
- Trisodium arsenate, Na3AsO4
- Disodium hydrogen arsenate, Na2HAsO4
References
- ↑ Grund, S. C.; Hanusch, K.; Wolf, H. U.. "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a03_113.pub2.
 |

