Chemistry:Disodium hydrogen arsenate
From HandWiki
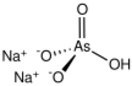
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Disodium hydrogen arsorate
| |
| Other names
Sodium arsenate dibasic
| |
| Identifiers | |
| ChEBI | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| Properties | |
| H15Na2AsO11 (heptahydrate) | |
| Molar mass | 312.01 g/mol (heptahydrate) |
| Appearance | white solid |
| good | |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | poison |
| GHS pictograms |   
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H301, H331, H350, H410 | |
| P201, P202, P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P281, P301+310, P304+340, P308+313, P311, P321, P330, P391, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Disodium hydrogen arsenate is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2HAsO4.7H2O. The compound consists of a salt and seven molecules of water of crystallization although for simplicity the formula usually omits the water component. The other sodium arsenates are NaH2AsO4 and Na3AsO4, the latter being called sodium arsenate. Disodium hydrogen arsenate is highly toxic. The salt is the conjugate base of arsenic acid. It is a white, water-soluble solid.[1]
Being a diprotic acid, its acid-base properties is described by two equilibria:
- H2AsO−4 + H2O ⇌ HAsO2−4 + H3O+ (pKa2 = 6.94)
- HAsO2−4 + H2O ⇌ AsO3−4 + H3O+ (pKa3 = 11.5)
Related compounds
- Monopotassium arsenate, KH2AsO4
References
- ↑ Grund, S. C.; Hanusch, K.; Wolf, H. U.. "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a03_113.pub2.
 |

