Chemistry:Mustakone
From HandWiki
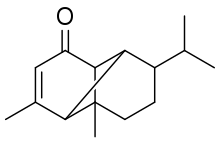
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1,5-dimethyl-8-propan-2-yltricyclo[4.4.0.02,7]dec-4-en-3-one
| |
| Other names
3-Copaen-2-one
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H22O | |
| Molar mass | 218.340 g·mol−1 |
| Boiling point | 128-129 °C[1] |
| Solubility | Soluble in cyclohexane[2] |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
Copaene |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Mustakone is a tricylic sesquiterpenoid with the chemical formula C15H22O. It is named after the plant it was first extracted from Cyperus rotundus, which had the common name "mustuka" in Hindi.[2] Mustakone can be found in a variety of plants and their oils like Myrcia sylvatica,[citation needed] Cyperus articulatus,[3] and Hymenaea courbaril.
References
- ↑ "Essential Oils from Leaves of Medicinal Plants of Brazilian Flora: Chemical Composition and Activity against Candida Species". Medicines 4 (2): 27. May 2017. doi:10.3390/medicines4020027. PMID 28930242.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Studies in sesquiterpenes—XXII: Structure of mustakone and copaene" (in en). Tetrahedron 21 (2): 607–618. January 1965. doi:10.1016/S0040-4020(01)82231-6.
- ↑ "Cyperus articulatus L. (Cyperaceae) Rhizome Essential Oil Causes Cell Cycle Arrest in the G2/M Phase and Cell Death in HepG2 Cells and Inhibits the Development of Tumors in a Xenograft Model". Molecules 25 (11): 2687. June 2020. doi:10.3390/molecules25112687. PMID 32527068.
 |
