Chemistry:N-Methylmorpholine
From HandWiki
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
4-Methylmorpholine
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| Abbreviations | NMM | ||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 2535 | ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C5H11NO | |||
| Molar mass | 101.149 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Liquid | ||
| Density | 0.92 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | −66 °C (−87 °F; 207 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 115 to 116 °C (239 to 241 °F; 388 to 389 K) | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 7.38 (for the conjugate acid) (H2O)[1] | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS pictograms |   
| ||
| GHS Signal word | Danger | ||
| H225, H302, H312, H314, H332 | |||
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+312, P301+330+331, P302+352, P303+361+353, P304+312, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P312, P321, P322, P330, P363 | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
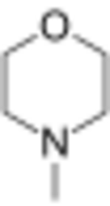
N-Methylmorpholine is the organic compound with the formula O(CH2CH2)2NCH3. It is a colorless liquid. It is a cyclic tertiary amine. It is used as a base catalyst for generation of polyurethanes and other reactions. It is produced by the reaction of methylamine and diethylene glycol as well as by the hydrogenolysis of N-formylmorpholine.[2] It is the precursor to N-methylmorpholine N-oxide, a commercially important oxidant.
References
- ↑ David Evans Research Group
- ↑ Karsten Eller; Erhard Henkes; Roland Rossbacher; Hartmut Höke (2005). "Amines, Aliphatic". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a02_001. ISBN 3-527-30673-0.
 |