Chemistry:N-Vinylacetamide
From HandWiki
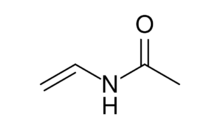
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
N-Ethenylacetamide | |
| Other names
N-Vinylacetamide
NVA N-Vinylcarboxylic acid amide N-Carboxylic acid amide Vinylamide NVA monomer | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H7NO | |
| Molar mass | 85.106 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Melting point | 54 °C (129 °F; 327 K) |
| Boiling point | 96 °C (205 °F; 369 K) |
| soluble | |
| Solubility in acetone | soluble |
| Solubility in ether | soluble |
| Solubility in ester | soluble |
| Solubility in arene | soluble |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H302, H315, H319 | |
| P264, P270, P280, P301+312, P302+352, P305+351+338, P321, P330, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P501 | |
| Flash point | 113 °C (235 °F; 386 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
N-Vinylacetamide (NVA) is a non-ionic monomer. Copolymers made of NVA and other monomers can exhibit practical characteristics in addition to those common with the existing hydrophilic polymers.
History
NVA is an amphipathic monomer. It was introduced and compounded in the U.S. in 1967. Today, it is recognized as a monomer that does polymerize; however, Showa Denko K.K. succeeded in its industrialization in 1997.[1]
Properties
NVA is soluble in water, various organic solvents and liquid vinyl monomers. It is polymerizable by various radical polymerization processes, depending on the objective. Since NVA itself is a solvent, it can act as a dissolution agent for poorly soluble substances.
References
 |
