Chemistry:Neopentylamine
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
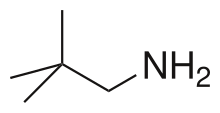
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2,2-dimethylpropan-1-amine
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H13N | |
| Molar mass | 87.166 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Density | 0.74 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −70 °C (−94 °F; 203 K) |
| Boiling point | 80–82 °C (176–180 °F; 353–355 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Irritant, Flammable, Corrosive |
| GHS pictograms |   
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H225, H302, H314 | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P260, P264, P270, P280, P301+312, P301+330+331, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P321, P330, P363, P370+378, P403+235, P405, P501 | |
| Flash point | -13 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Neopentylamine is an organic compound with the molecular formula (CH3)3CCH2NH2. It is a colorless liquid. The molecule is the primary amine derivative of neopentane, (CH3)4C.
Like most alkyl amines, it degrades slowly in air.[1]
Synthesis
Neopentylamine is prepared by the reaction neopentanol with ammonia.[2]
Use
It is a common building block.[3] For example, some experimental drugs incorporate this amine.[4][5]
References
- ↑ "Neopentylamine 5813-64-9 | Tokyo Chemical Industry UK Ltd.". https://www.tcichemicals.com/GB/en/p/N0505.
- ↑ Werner, Friedrich; Heinz U. Blank & Gunther Gramm et al., "Process for the preparation of neopentylamine", US patent 4495369, published 1985-01-22, issued 1981-09-22
- ↑ "Neopentylamine Safety Data Sheet". https://www.fishersci.com/store/msds?partNumber=AC173690250&productDescription=NEOPENTYLAMINE%2C+97%25+25ML&vendorId=VN00032119&countryCode=US&language=en.
- ↑ Biamonte, Marco A.; Shi, Jiandong; Hong, Kevin; Hurst, David C.; Zhang, Lin; Fan, Junhua; Busch, David J.; Karjian, Patricia L. et al. (2006). "Orally Active Purine-Based Inhibitors of the Heat Shock Protein 90". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 49 (2): 817–828. doi:10.1021/jm0503087. PMID 16420067.
- ↑ Fraser, Robert R.; Mansour, Tarek S. (1984). "Acidity measurements with lithiated amines: Steric reduction and electronic enhancement of acidity". The Journal of Organic Chemistry 49 (18): 3442–3443. doi:10.1021/jo00192a059.

