Chemistry:Nerolic acid
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
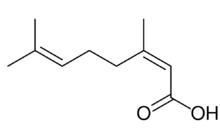
| Preferred IUPAC name
(2Z)-3,7-Dimethylocta-2,6-dienoic acid | |
| Other names
Neric acid; 3,7-Dimethylocta-2,6-dienoic acid; 3,7-Dimethyl-2,6-octadienoic acid,
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H16O2 | |
| Molar mass | 168.236 g·mol−1 |
| Related compounds | |
Related isomers
|
Geranic acid |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Nerolic acid, also known as (Z)-3,7-Dimethyl-2,6-octadienoic acid, is an organically-derived chemical.
In nature
Nerolic acid is found in the Nasonov scent gland of honey-bees along with geraniol, geranic acid, citral, farnesol, and nerol. Of these, nerolic acid, geraniol, and farnesol are present in the highest proportions.[1][2][3].
It is one of the five compounds that are part of the essential oils of Myrcia Ovata.[4]
It is a compound also found in great quantity in Myrcia lundiana and it possess antifungal properties against pathogens such as Fusarium solani, and Lasiodiplodia theobromae.[5] Both Myrcia Ovata and Myrcia lundiana are part of the Myrtaceae family plant, both containing a certain percentage of Nerolic acid compound.[4][5]
In addition to this, Nerolic acid is also a principal chemical compound of essential oils of lemongrass, and is also believed to possess antifungal properties. [6]
References
- ↑ Winston, Mark L (1987). The Biology of the Honey Bee. First Harvard University Press. p. 37. ISBN 978-0-674-07409-5.
- ↑ R Boch; DA Shearer (April 18, 1964). "Identification of Nerolic and Geranic Acids in the Nassanoff Pheromone of the Honey Bee". Nature 202 (4929): 320–321. doi:10.1038/202320a0. Bibcode: 1964Natur.202..320B.
- ↑ "Evalutation of Various Components of the Nasonov Pheromone used by clustering honeybees". Physiological Entomology 6 (3): 263–268. 1981. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3032.1981.tb00270.x.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 White, Larissa Alves Secundo; Blank, Arie Fitzgerald; Gagliardi, Paulo Roberto; Arrigoni-Blank, Maria de Fátima; Nizio, Daniela Aparecida de Castro; Sampaio, Taís Santos; Alves, Mércia Freita; Almeida-Pereira, Camila Santos (2019-10-15). "In vitro antifungal activity of Myrcia ovata essential oils and their major compounds against pathogens of citrus, sweet potato, and coconut" (in en). Bioscience Journal 35 (6): 1696. doi:10.14393/BJ-v35n6a2019-42425. ISSN 1981-3163. https://seer.ufu.br/index.php/biosciencejournal/article/view/42425.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Alves, Mércia Freitas; Nizio, Daniela Aparecida de Castro; Sampaio, Taís Santos; Nascimento, Alberto Ferreira do; Brito, Fabiany de Andrade; Melo, Juliana Oliveira de; Arrigoni-Blank, Maria de Fátima; Gagliardi, Paulo Roberto et al. (2016-07-01). "Myrcia lundiana Kiaersk native populations have different essential oil composition and antifungal activity against Lasiodiplodia theobromae" (in en). Industrial Crops and Products 85: 268. doi:10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.03.039. ISSN 0926-6690. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0926669016301856.
- ↑ Sargenti, S. R.; Lanças, F. M. (1997-09-01). "Supercritical fluid extraction ofCymbopogon citratus (DC.) Stapf" (in en). Chromatographia 46 (5): 286. doi:10.1007/BF02496320. ISSN 1612-1112. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02496320.
 |

