Chemistry:Oxamic acid
From HandWiki
| |
 Ball and stick model of oxamic acid
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Oxamic acid[1] | |
| Other names
Amino(oxo)acetic acid[1]
2-Amino-2-oxoacetic acid 2-oxoglycine Aminooxoacetic acid Oxalamic acid Oxamidic acid 2-Amino-2-oxoethanoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
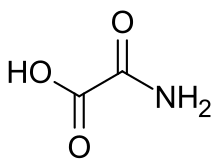
| NH 2C(O)COOH | |
| Molar mass | 89.050 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Melting point | 209 °C[2] |
| Soluble | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P264+265Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P271, P280, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P319Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P321, P332+317Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P337+317Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P362+364Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Oxamic acid is an organic compound with the formula NH
2C(O)COOH. It is a white, water-soluble solid. It is the monoamide of oxalic acid.[3] Oxamic acid inhibits lactate dehydrogenase A.[4] The active site of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) is closed off once oxamic acid attaches to the LDH-NADH complex, effectively inhibiting it.[5]
Oxamic acid also has applications in polymer chemistry. It increases the water solubility of certain polymers, including polyester, epoxide, and acrylic upon binding with them.[6]
See also
- Oxamate, the conjugate base of oxamic acid
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. p. 415. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ↑ CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (92nd ed.). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. 2011. p. 3.430. ISBN 978-1-4398-5511-9. https://archive.org/details/crchandbookofche00davi.
- ↑ "Oxamic acid". PubChem. National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/oxamic_acid#section=Depositor-Supplied-Synonyms.
- ↑ "Synergistic anti-cancer effect of phenformin and oxamate". PLOS ONE 9 (1). 2014. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0085576. PMID 24465604. Bibcode: 2014PLoSO...985576M.
- ↑ Raczyńska, Ewa D.; Hallmann, Małgorzata; Duczmal, Kinga (March 2011). "Quantum-chemical studies of amide–iminol tautomerism for inhibitor of lactate dehydrogenase: Oxamic acid". Computational and Theoretical Chemistry 964 (1–3): 310–317. doi:10.1016/j.comptc.2011.01.017. ISSN 2210-271X.
- ↑ Zarzyka-Niemiec, Iwona (2008-10-05). "Hydroxyalkylation of oxamic acid with propylene carbonate: Synthesis, composition, and properties of products". Journal of Applied Polymer Science 110 (1): 66–75. doi:10.1002/app.28609. ISSN 0021-8995. Bibcode: 2008JAPS..110...66Z.
 |
