Chemistry:Perchlorylbenzene
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(Trioxo-λ7-chloranyl)benzene
| |
| Other names
Phenyltrioxo-λ7-chlorane
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
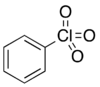
| C6H5ClO3 | |
| Molar mass | 160.55 g·mol−1 |
| Boiling point | 232 °C (450 °F; 505 K) (78 °C @ 2 mmHg) |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Explosive |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Perchlorylbenzene (C6H5ClO3, PhClO3, is an aromatic compound prepared by direct electrophilic perchlorylation of benzene using perchloryl fluoride and aluminum trichloride:[1]
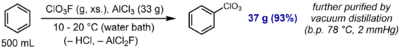
The compound is described as a somewhat shock-sensitive oily liquid. It exhibits low chemical reactivity and is inert towards acidic (HCl (aq.)) or reducing (LiAlH4, H2/Pd) conditions. However, it undergoes hydrolysis upon reflux in aqueous KOH to afford phenol, and undergoes aromatic nitration to afford the meta-nitration product, as expected for a strongly –I, –M substituent.
It and its derivatives have been investigated as novel energetic materials analogous to nitro compounds.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ Inman, C. E.; Oesterling, R. E.; Tyczkowski, E. A. (1958-10-01). "Reactions of Perchloryl Fluoride with Organic Compounds. I. Perchlorylation of Aromatic Compounds1". Journal of the American Chemical Society 80 (19): 5286–5288. doi:10.1021/ja01552a069. ISSN 0002-7863.
- ↑ Ledgard, Jared (2007). The Preparatory Manual of Explosives. ISBN 9780615142906.
 |

