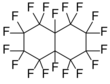
Chemistry:Perfluorodecalin
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Octadecafluorodecahydronaphthalene | |||
| Other names
Flutec PP6
F-decalin Perflunafene | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
| ||
| Abbreviations | PFD | ||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| EC Number |
| ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C10F18 | |||
| Molar mass | 462 | ||
| Appearance | Clear, colorless liquid | ||
| Density | 1.917 | ||
| Boiling point | 142 °C (288 °F; 415 K) | ||
| 10 ppm | |||
| Hazards | |||
| Main hazards | None | ||
| Flash point | None | ||
| None | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Perfluorodecalin (C
10F
18) is a fluorocarbon, a derivative of decalin in which all of the hydrogen atoms are replaced by fluorine atoms. It is chemically and biologically inert and stable up to 400 °C. Several applications make use of its ability to dissolve gases.
Manufacture
It is manufactured by the fluorination of tetralin or decalin with cobalt(III) fluoride in the Fowler process. For most applications, several steps of purification are required after reaction.
Isomers
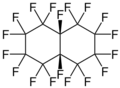
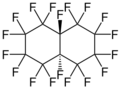
Perfluorodecalin exhibits cis-trans isomerism, as the tertiary fluorines atoms on the bridge carbon atoms can be either on the same side as each other (cis-isomer) or on opposite sides (trans-isomer). Both isomers are chemically and biologically inert and are very similar in their physical properties. The most notable difference is in the melting point, which is −3.6 °C for the cis-isomer, +18 °C for the trans-isomer, and −6.7 °C for a 50/50 mixture.[1]
-
cis
-
trans
Medical applications
Of all the perfluorocarbons, perfluorodecalin has probably seen the most interest in medical applications. Most applications utilize its ability to dissolve large amounts of oxygen (100 mL of perfluorodecalin at 25 °C can dissolve 49 mL of oxygen at STP[2]).
Perfluorodecalin was an ingredient in Fluosol, an artificial blood product developed by Green Cross Corporation in the 1980s. It is also being studied for use in liquid breathing. Perfluorodecalin can be applied topically, to provide extra oxygen to a specific location, to accelerate wound healing. Organs and tissues can be stored for longer in oxygenated perfluorodecalin; the "two-layer method" uses perfluorodecalin and UW solution to preserve tissue for pancreas transplants.[3]
It is an ingredient of Perftoran, a blood substitute that also contains perfluoro-N-(4-methylcyclohexyl)-piperidine along with a surfactant, proxanol-268. It was developed in Russia and as of 2005 was marketed there.[4]
Other applications
Due to its gas-carrying capacity, perfluorodecalin has been used to enhance oxygen delivery during cell culture.[5] Perfluorodecalin has also been shown to dramatically enhance in vivo microscopy resolution of airspace-containing tissues such as mesophyll. Mounting leaves in perfluorodecalin significantly improves the optical qualities of the leaf, thereby enabling high-resolution imaging over twofold deeper into the mesophyll, compared with using water. The physiological impact of mounting the specimen in perfluorodecalin is also minimal compared to water.[6]
Perfluorodecalin is partially miscible with hydrocarbons[7] which makes it an attractive inert anti-solvent for some specialized applications, such as self-organization of perovskite nanocrystals into supercrystals (also known as superlattices).[8]
This compound is sometimes used to dissolve Teflon AF[9] (not to be confused with other Teflons, as PTFE, PFA and FEP).
References
- ↑ "Flutec PP Fluorocarbon Liquids", ISC Chemicals Ltd, table E5-2/4
- ↑ "Perfluorodecalin". F2 Chemicals Ltd. http://www.f2chemicals.com/pdf/technical/Gas%20solubility.pdf.
- ↑ For instance, Witkowski, P.; Liu, Z.; Guo, Q.; Poumian-Ruiz, E.; Cernea, S.; Herold, K.; Hardy, M.A. (2005). "Two-Layer Method in Short-Term Pancreas Preservation for Successful Islet Isolation". Transplantation Proceedings 37 (8): 3398–401. doi:10.1016/j.transproceed.2005.09.050. PMID 16298606.
- ↑ Maevsky, E; Ivanitsky, G; Bogdanova, L; Axenova, O; Karmen, N; Zhiburt, E; Senina, R; Pushkin, S et al. (2005). "Clinical results of Perftoran application: present and future.". Artificial Cells, Blood Substitutes, and Biotechnology 33 (1): 37–46. doi:10.1081/BIO-200046654. PMID 15768564.
- ↑ King, A. T.; Mulligan, B. J.; Lowe, K. C. (1989). "Perfluorochemicals and Cell Culture". Nature Biotechnology 7 (10): 1037–1042. doi:10.1038/nbt1089-1037.
- ↑ Littlejohn, George R.; Gouveia, João D.; Edner, Christoph; Smirnoff, Nicholas; Love, John (2010). "Perfluorodecalin enhances in vivo confocal microscopy resolution of Arabidopsis thaliana mesophyll". New Phytologist 186 (4): 1018–25. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03244.x. PMID 20374500. https://pearl.plymouth.ac.uk/bitstream/10026.1/9344/1/Littlejohn_et_al-2010-New_Phytologist.pdf.
- ↑ Bernardo-Gil, Gabriela S.; Soares, Luis J. S. (July 1, 1987). "Mutual binary solubilities: perfluorodecalin/hydrocarbons" (in en). Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data 32 (3): 327–329. doi:10.1021/je00049a014. ISSN 0021-9568.
- ↑ Baranov, Dmitry; Toso, Stefano; Imran, Muhammad; Manna, Liberato (2019-02-07). "Investigation into the Photoluminescence Red Shift in Cesium Lead Bromide Nanocrystal Superlattices" (in en). The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters 10 (3): 655–660. doi:10.1021/acs.jpclett.9b00178. ISSN 1948-7185. PMID 30676762.
- ↑ "Teflon AF". Sigma Aldrich. http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/aldrich/469629?lang=en®ion=US.
External links
 |