Chemistry:Picramic acid
From HandWiki
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
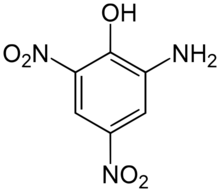
2-Amino-4,6-dinitrophenol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 3317 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H5N3O5 | |
| Molar mass | 199.12 g/mol |
| Appearance | Brown paste |
| Density | 1.749 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 169 °C (336 °F; 442 K) |
| Boiling point | 386.3 °C (727.3 °F; 659.5 K) |
| log P | 2.41840[1] |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.73 [1] |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H201, H302, H312, H332, H412 | |
| P210, P230, P240, P250, P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P301+312, P302+352, P304+312, P304+340, P312, P322, P330, P363, P370+380, P372, P373, P401, P501 | |
| Flash point | 187.5 °C (369.5 °F; 460.6 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Picramic acid, also known as 2-amino-4,6-dinitrophenol,[3] is an acid obtained by neutralizing an alcoholic solution of picric acid with ammonium hydroxide. Hydrogen sulfide is then added to the resulting solution, which turns red, yielding sulfur and red crystals. These are the ammonium salts of picramic acid, from which it can be extracted using acetic acid.[4] Picramic acid is explosive and very toxic. It has a bitter taste.[5]
Along with its sodium salt (sodium picramate) it is used in low concentrations in certain hair dyes, such as henna, it is considered safe for this use provided its concentration remains low.[6]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Picramic acid". https://www.chemsrc.com/en/cas/96-91-3_670346.html.
- ↑ "2-Amino-4,6-dinitrophenol" (in en). https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/4921319#section=Safety-and-Hazards.
- ↑ "Haz-Map Category Details". http://hazmap.nlm.nih.gov/category-details?id=3267&table=copytblagents.
- ↑ "Archived copy". http://www.jbc.org/content/35/3/565.full.pdf.
- ↑ "PICRAMIC ACID (2-AMINO-4,6-DINITROPHENOL)". http://chemicalland21.com/specialtychem/perchem/PICRAMIC%20ACID.htm.
- ↑ "Final Report on the Safety Assessment of Sodium Picramate". Journal of the American College of Toxicology 11 (4): 447–464. July 1992. doi:10.3109/10915819209141884.
 |

