Chemistry:Pivaldehyde
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,2-Dimethylpropanal | |
| Other names
Trimethylacetaldehyde
Pivalaldehyde Neopentanal Neopentaldehyde | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| (CH3)3CCHO | |
| Molar mass | 86.13 g/mol |
| Boiling point | 74–76 °C (165–169 °F; 347–349 K)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H225, H315, H335 | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+352, P303+361+353, P304+340, P312, P321, P332+313, P362, P370+378, P403+233, P403+235, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
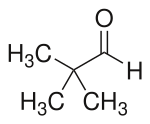
Pivaldehyde is an organic compound, more specifically an aldehyde. Shown in the image is a line-angle representation of this organic aldehyde, whose systematic name, 2,2-dimethylpropanal, is based on the longest carbon chain (three carbon atoms), ending in "-al" to indicate the aldehyde functionality, and where another descriptive synonym is trimethylacetaldehyde.[2] Pivaldehyde is an example of an aldehyde with a sterically bulky R group, the tertiary-butyl group (with 3 methyl groups, at lower left in the image), attached to the carbonyl, >C=O. By definition, the other "group", R', is a hydrogen (H) atom, shown here pointing directly upward.
See also
- Pivalic acid - corresponding carboxylic acid
- Pivalamide - corresponding amide
- Pinacolone - corresponding methyl ketone
References
- ↑ Conant, J. B.; Webb, C. N.; Mendum, W. C. (April 1929). "TRIMETHYLACETALDEHYDE AND DIMETHYLETHYLACETALDEHYDE". Journal of the American Chemical Society 51 (4): 1246–1255. doi:10.1021/ja01379a038.
- ↑ Pubchem. "Trimethylacetaldehyde". nih.gov. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/12417#section=Top. Retrieved 1 March 2016.
 |
