Chemistry:Pivaloyl chloride
From HandWiki
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
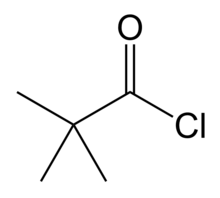
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,2-Dimethylpropanoyl chloride | |
| Other names
Trimethylacetyl chloride; Pivaloyl chloride; Pivalyl chloride; neopentanoylchloride
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 102382 | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2438 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H9ClO | |
| Molar mass | 120.58 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.985 |
| Melting point | −57 °C (−71 °F; 216 K) |
| Boiling point | 105.5 °C (221.9 °F; 378.6 K) |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.412 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |    
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H225, H290, H302, H314, H330 | |
| P210, P233, P234, P240, P241, P242, P243, P260, P264, P270, P271, P280, P284, P301+312, P301+330+331, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P320, P321, P330, P363, P370+378, P390 | |
| Flash point | 8 °C (46 °F; 281 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
2,2-Dimethylpropanoyl chloride is a branched-chain acyl chloride.[1] It was first made by Aleksandr Butlerov in 1874 by reacting pivalic acid with phosphorus pentachloride.[2]
Pivaloyl chloride is used as an input in the manufacture of some drugs, insecticides and herbicides.
References
- ↑ "2,2-dimethylpropanoyl chloride". http://www.chemsynthesis.com/base/chemical-structure-40091.html. Retrieved 1 July 2017.
- ↑ Buttlerow, A. (1874). "Ueber die Trimethylessigsäure". Justus Liebig's Annalen der Chemie 173 (2): 355–375. doi:10.1002/jlac.18741730217. https://zenodo.org/record/1427337.
 |

