Chemistry:Poly(butyl acrylate)
From HandWiki
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| Properties | |
| Appearance | colorless solid |
| Density | 1.06 g/cm3 |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.474 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
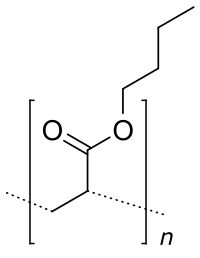
Poly(butyl acrylate) (PBA) is a family of organic polymers with the formula (CH
2CHCO
2CH
2CH
2CH
2CH
3)n. It is a synthetic acrylate polymer derived from butyl acrylate monomer. The polymers are colorless. This homopolymer is far less important than copolymers derived from methyl acrylate and other monomers. It has a low glass-transition temperature of about -43 °C (20 °C).[clarification needed]
Copolymers
Far more important than PBA are copolymers produced from butyl acrylate and one or more of the following comonomers methyl methacrylate, styrene, acrylonitrile, vinyl acetate, vinyl chloride, vinylidene chloride, and butadiene.[1]
References
- ↑ Penzel, Erich; Ballard, Nicholas; Asua, José M. (2018). "Polyacrylates". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. pp. 1–20. doi:10.1002/14356007.a21_157.pub2. ISBN 9783527306732.
 |

