Chemistry:Propylene chlorohydrin
From HandWiki
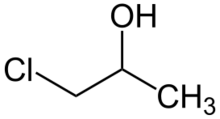
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-Chloropropan-2-ol | |
| Other names
1-Chloro-2-hydroxypropane
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H7ClO | |
| Molar mass | 94.54 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Density | 1.1154 g/mL |
| Boiling point | 127°C |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H226, H302, H315, H319, H332, H335 | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+312, P302+352, P303+361+353, P304+312, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P330, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P370+378, P403+233 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Propylene chlorohydrin usually refers to the organic compound with the formula CH3CH(OH)CH2Cl. A related compound, an isomer, is CH3CH(Cl)CH2OH. Both isomers are colorless liquids that are soluble in organic solvents. They are classified as chlorohydrins. Both are generated on a large scale as intermediates in the production of propylene oxide.[1]
The reaction of aqueous solution of chlorine with propene gives a 10:1 ratio of CH3CH(OH)CH2Cl and CH3CH(Cl)CH2OH. These compounds are treated with lime to give propylene oxide, which is useful in the production of plastics and other polymers.
References
- ↑ Gordon Y. T. Liu, W. Frank Richey, Joanne E. Betso, Brian Hughes, Joanna Klapacz, and Joerg Lindner "Chlorohydrins" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2014, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a06_565.pub2
 |
